Compressors
6.17k likes | 16.19k Vues
Compressors. What is a Compressor? A mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume . Similar to a pump – Increases the pressure on a fluid and transport it through a pipe. What is key difference between a Fluid and a Gas?

Compressors
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Compressors • What is a Compressor? • A mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. • Similar to a pump – Increases the pressure on a fluid and transport it through a pipe. • What is key difference between a Fluid and a Gas? • Compressibility – a gas is compressible • What happens to gas volume as it is compressed? • Decreases • What happens to the Temperature of the Gas as it is compressed? • Increases
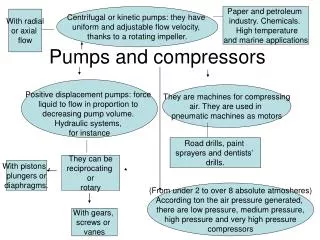
Compressors • Compressors are classified by how they work • Two Categories of Compressors • Positive Displacement • Dynamic • What is a Positive Displacement Compressor? • A compressor that confines successive volumes of gas within a closed space in which the pressure of the gas is increased as the volume of the closed space is decreased. • Intermittent Flow • What is a Dynamic Compressor? • A compressor using a rotating mechanism to add velocity and pressure to gas. • Continuous Flow
Compressors • Two types of Positive Displacement Compressors: • Reciprocating • Rotary • Two Types of Dynamic Compressors • Centrifugal • Axial
Compressors • Reciprocating Compressors • How does it work? • Piston movement in a cylinder connected to a rod and crankshaft • Downward piston motion, low pressure gas enters the chamber • Upward piston motion, gas is compressed and exits the chamber • Video
Compressors • Reciprocating Compressors • High Horsepower Applications • Common in natural gas transmission lines. • Processes for high pressure delivery of gasses • Air Conditioning Compressors • Some manufactures (Frigidaire™) use rotary compressors • AC Compressors (and other small appliance applications) are Hermetic or Semi-Hermetic
Compressors • Hermetically Sealed and Semi Hermetically Sealed Compressors • The compressor and motor driving the compressor are integrated, and operate within the pressurized gas envelope of the system. • The motor is designed to operate and be cooled by the gas or vapor being compressed. • The hermetic uses a one-piece welded steel casing that cannot be opened for repair. • If the hermetic fails it is simply replaced with an entire new unit. • A semi-hermetic uses a large cast metal shell with gasketed covers that can be opened to replace motor and pump components. • The primary advantage of a hermetic and semi-hermetic is that there is no route for the gas to leak out of the system. • Open compressors rely on either natural leather or synthetic rubber seals to retain the internal pressure • Require a lubricant such as oil to retain their sealing properties
Compressors • Rotary Compressors • How do they it work? • When a rotating mechanism spins past the inlet valve, it creates a vacuum. • The fluid flows out of the valve behind it, filling the vacuum. • As it approaches the outlet valve, the chamber shrinks, creating more pressure on the fluid. • The fluid has nowhere to go but out of the outlet valve, so it shoots out of it. • Then the rotating mechanism continues on to draw more fluid at the inlet valve. • How it works Video
Compressors • Common Types of Rotary Compressors • Screw • Vane • Scroll • Screw • Two meshing helix screws • Rotors • Compact and smooth running • 2 types - Oil Free and Oil Flooded • Oil Free – No assistance from oil to cool and assist in sealing . • Oil Flooded – Oil injected to aid in sealing and provide cooling. • Separator downstream to capture the oil
Compressors • Vane Compressors • Vane housing on a off centered shaft • Vanes slide in an out always making contact with the compressor walls • Gas enters in the largest opening • Exits the smallest • Good for low pressure applications • Efficient • Heat controlled by oil injection
Compressors • Scroll Compressor • How it works • 2 Spirals • 1 stationary, 1 orbits without rotating • 1st orbit entraps inlet gas • Subsequent orbits compresses gas and exited out the center • Generally 2-3 orbits for a full cycle • Video • Advantages • Compact • Steady flow • Low energy use • Quiet • Smooth operation
Compressors • What is a Dynamic Compressor? • A compressor using a rotating mechanism to add velocity and pressure to gas. • Continuous Flow • What are the Two Types of Dynamic Compressors? • Centrifugal • Axial
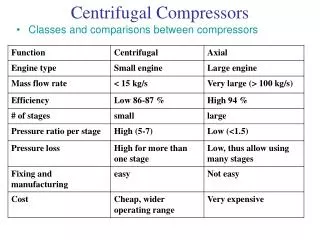
Compressors • Centrifugal Compressors • Rotating disk (impeller) forces gas to the rim of the impeller, increasing velocity • The diffuser converts the velocity energy to pressure energy. • Primarily used for continuous, stationary service in industries such as refineries, chemical plants and snow making operations • Single Stage and Multi-Stage Compressors • How a Centrifugal Compressor Works
Compressors • Impeller • Most critical part of a centrifugal compressor • Compressor performance determined by impeller: • Size • Shape • Speed • 3 types of Impellers • Closed • Most common • Shroud covering both sides of the blade • Center eye hole for gas to enter • Used in Multi-stage compressors • Semi –open • Open
Compressors • Multi-Stage Compressors • Diaphragm • Specially designed casing wall separating the stages • Gas passes through the difuser • Passes through the return channel in the diaphragm • Controlling Axial Load on the Shaft • Bearing Review • Thrust Bearing
Compressors • Axial Compressors • Gas flows parallel to the axis of rotation • Unlike centrifugal that has radial components • Has rotating and stationary components • Rotating airfoil – rotor • Stationary airfoil – stator • Similar number of these on a shaft Video
Compressors • Axial Compressors • High Volume • High Efficiency • High Cost • Common Uses • Gas Turbines • Jet engines • Power stations • Nickname – “Superchargers”
Homework • What is a Compressor? • What happens to the temperature and the volume of a gas as it is compressed? • What are the 2 categories of Compressors? • Explain the difference between a positive displacement and radial compressor. • Explain how a reciprocating compressor works. • Describe a Hermetically sealed compressor. • Explain how a rotary compressor works. • Describe how a scroll compressor works. • Explain how a multi stage compressor works. • What type of compressor is found on jet aircraft?