Playing Tonk Statistically
230 likes | 392 Vues
Playing Tonk Statistically. By: Akash Levy. Introduction. Statistics from a historical perspective What is tonk? What are its rules? How can we use statistics to play tonk profitably?. Rules of Allderdice Tonk.

Playing Tonk Statistically
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Playing Tonk Statistically By: Akash Levy
Introduction • Statistics from a historical perspective • What is tonk? • What are its rules? • How can we use statistics to play tonk profitably?
Rules of Allderdice Tonk • Each player is dealt 5 cards (sometimes 7). Play usually proceeds clockwise, starting left of the dealer. • Each turn, a player picks up a card from either the deck or the discard pile or “drops”. • The player must then discard a card in his or her hand. Before discarding, this player can play down a “spread” which is either 3 or 4 cards of the same rank (ex: 4H, 4D, 4C or QH, QD, QC, QS) or three or more consecutive cards from the same suit (ex: 4H, 5H, 6H or 10C, JC, QC, KC). A player can also “hit” an existing spread, meaning adding another card to an existing spread. A player whose hand is hit cannot drop for a number of turns equivalent to the number of cards added to the spread.
More Rules of Allderdice Tonk • The goal of the game is to get rid of all of the cards in your hand or “drop” successfully. In Allderdice tonk, the last person with cards in his or her hand (the loser) pays the first person to have no cards in his or her hand (the winner). • “Dropping” means putting the cards in your hand on the table with the challenge that nobody is “lower” than you. To calculate how low you are, you add up the points in your hand where aces are one point, 2-9 are a number of points corresponding to the number on the card and 10, J, Q, K (also known as bricks) are ten points. If you drop and have the lowest hand, you win one unit of money from the loser, but if someone else is lower than you (“catches” you), you pay that person one unit of money. This means that if you are playing against just one other player and you “get caught”, you lose two dollars. With more than two players, the play continues and the loser also pays the winner. • In Allderdice tonk, starting with a hand with all bricks is called a “tonk”. A player who gets a tonk automatically wins. • Also, if a player plays down all of their spreads at once before anyone else wins, it is called a “bonkey”. The person who bonkeys is payed two units of money by the loser.
My Objectives • Discover how low you should be to drop on the first turn with: • 5 cards, one other player • 7 cards, one other player
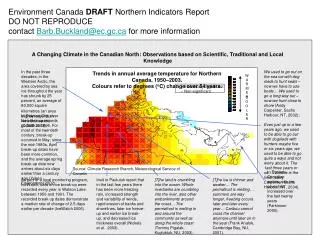
Plan for finding profitable first-turn drop • Our calculations can only serve as an approximation because actual calculations are incredibly complicated • One assumption we cannot make is independence assumption • We are going to make this assumption anyways to simplify calculations (by using a normal model) • What is the approximate mean and standard deviation?
Mean • Expected value for one card: • Expected value for five cards assuming independence of card values: • Expected value for seven cards assuming independence of card values: Note: Expected values for five cards and seven cards are approximations because we assume independence.
Standard Deviations • Standard deviation for one card: • Approximate standard deviation for five cards (assuming independence): • Approximate standard deviation for seven cards (assuming independence): • Note: The more cards we use, the more normal the distribution becomes.
Calculating expected pay for one other player • Five cards: • Seven cards:
Calculating points in terms of expected pay • So when should we drop when playing against one player?
Calculating points in terms of expected pay • Five cards, one person: • Seven cards, one person:
Approximations? Why not exact answers? • The more complicated question • What we can and can’t reasonably do • Using an exact model • Why lack of independence is almost impossible to solve
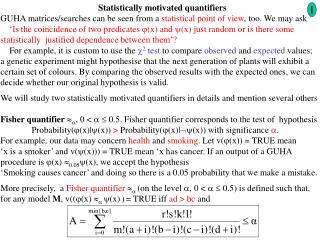
The exact answer (not using normal model) • Mark Gritter’s post on twoplustwo forum • Contacted him • Got reply on how to find the exact answer • Binomial model except calculations are more complicated • Independence is not factored in (as before) • Generating functions
The generating function for the situation • G(x,y) = (1+yx)(1+yx)(1+yx)(1+yx)(1+yx^2)(1+yx^2)....(1+yx^10) The full version: (1+y x)^4 (1+y x^2)^4 (1+y x^3)^4 (1+y x^4)^4 (1+y x^5)^4 (1+y x^6)^4 (1+y x^7)^4 (1+y x^8)^4 (1+y x^9)^4 (1+y x^10)^16 • When expanded, the coefficients of the y^5 term represent the ways to pick five cards, the coefficients of the y^7 term represent the ways to pick seven cards
How we go about finding the coefficients • Wolfram Mathematica, of course expr := (1 + y x)^4 (1 + y x^2)^4 (1 + y x^3)^4 (1 + y x^4)^4 (1 + y x^5)^4 (1 + y x^6)^4 (1 + y x^7)^4 (1 + y x^8)^4 (1 + y x^9)^4 (1 + y x^10)^16 Coefficient[Expand[expr], y, n] Where n is the number of cards in a hand
5 card coefficients 4 x6+28 x7+92 x8+240 x9+484 x10+920 x11+1552 x12+2492 x13+3784 x14+5724 x15+8344 x16+11988 x17+16520 x18+22144 x19+28948 x20+36708 x21+45584 x22+55712 x23+67600 x24+79416 x25+92416 x26+103808 x27+115520 x28+125188 x29+134052 x30+140224 x31+146936 x32+149268 x33+147784 x34+143676 x35+136344 x36+127484 x37+116832 x38+105176 x39+92548 x40+82176 x41+65532 x42+52556 x43+40436 x44+31216 x45+22496 x46+16720 x47+10640 x48+7280 x49+4368 x50
7 card coefficients 4 x10+28 x11+112 x12+324 x13+816 x14+1756 x15+3500 x16+6412 x17+11244 x18+18808 x19+30708 x20+48248 x21+74192 x22+110616 x23+160820 x24+227920 x25+316304 x26+430120 x27+574284 x28+753648 x29+969672 x30+1229020 x31+1527544 x32+1869768 x33+2249888 x34+2672392 x35+3121136 x36+3599624 x37+4081096 x38+4564636 x39+5027272 x40+5458256 x41+5838524 x42+6166904 x43+6420560 x44+6581968 x45+6655796 x46+6617080 x47+6491440 x48+6265512 x49+5963204 x50+5579928 x51+5158940 x52+4665228 x53+4152412 x54+3625196 x55+3110448 x56+2614660 x57+2163248 x58+1742460 x59+1378308 x60+1061616 x61+780240 x62+564256 x63+395056 x64+268128 x65+172368 x66+109200 x67+58240 x68+32032 x69+11440 x70
How good was the approximation using the normal model? • Pretty good, actually. • If we compare some values: Probability of getting caught (normal model) for 24 points, 5 cards: 0.1088 Probability of getting caught (exact) for 24 points, 5 cards: 0.1188 Approximate Difference: 0.0100 Probability of getting caught (normal model) for 35 points, 7 cards: 0.09835 Probability of getting caught (exact) for 35 points, 7 cards: 0.09932 Approximate Difference: 0.00097 • Nice!
Additional calculations just for fun • Probability of getting a tonk with 5 cards: • Probability of getting a tonk with 7 cards: • Probability of getting a tonk with n cards:
Thank you! Credits/Links: • http://www.learningpythonprogramming.com/2011/03/python-card-games.html • http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.std.html • http://forumserver.twoplustwo.com/25/probability/tonk-odds-dropping-issues-1277060/ • http://forumserver.twoplustwo.com/21/draw-other-poker/profitably-dropping-tonk-315444/ • http://www.pagat.com/rummy/tonk.html • http://markgritter.livejournal.com/711360.html • http://pastebin.com/cF9jG2BA