DECOMPOSITION
90 likes | 266 Vues
This study explores the interface characteristics between a cap layer and a Stress-Activated Composite (SAC) using a traction-separation relationship. By integrating SAC decomposition with the mechanical deformation of both layers, key parameters are analyzed, including displacement and interaction force. Employing beam theory and the Winkler model, this work sets boundary conditions and utilizes Lennard-Jones interactions to define material properties. Initial conditions are established with specified elastic moduli and thicknesses for precise modeling of the interface behavior.

DECOMPOSITION
E N D
Presentation Transcript
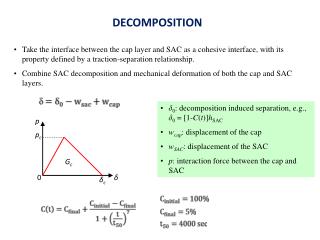
DECOMPOSITION • Take the interface between the cap layer and SAC as a cohesive interface, with its property defined by a traction-separation relationship. • Combine SAC decomposition and mechanical deformation of both the cap and SAC layers. • δ0: decomposition induced separation, e.g., δ0 = [1-C(t)]hSAC • wcap: displacement of the cap • wSAC: displacement of the SAC • p: interaction force between the cap and SAC p pc Gc 0 δ δc
DECOMPOSITION • Beam Theory for Cap w p(x) p(x) • Winkler Model for SAC C(t)hSAC • Boundary Condition (at x=0, L)
DECOMPOSITION • Lennard Jones Interaction • Material Property & Initial Condition Ecap= 9500 Mpa / ESAC= 6000 Mpa L=1000 nm, hCap = 200 nm , hSAC = 200 nm ro= 10nm
DECOMPOSITION 2 • Beam Theory for Cap & Winkler Model for SAC • Separating Displacement (since wcap=0 at x=0, L)