Neurodegenerative Disorders
350 likes | 703 Vues
Neurodegenerative Disorders. Huntington’s disease Parkinson’s disease Amylotrophic lateral sclerosis Alzheimer’s Disease. Some Facts. Degenerative brain disorder developed in adulthood (brain cells die) Progressive and irreversible decline in memory and other cognitive abilities

Neurodegenerative Disorders
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Neurodegenerative Disorders • Huntington’s disease • Parkinson’s disease • Amylotrophic lateral sclerosis • Alzheimer’s Disease
Some Facts • Degenerative brain disorder developed in adulthood (brain cells die) • Progressive and irreversible decline in memory and other cognitive abilities • ~4.5 million people in America
Symptoms • Forgetfulness and loss of smell • Memory loss becomes more severe • Language, perceptual, and motor skills deteriorate • Mood becomes unstable • Lost of mobility and control of body functions • Death http://www.alzheimers.org/rmedia/mediaroom.htm#animation
Diagnosis • Diagnosis by exclusion • Medical history and mental status exams • Physical examination • Neurological exam • Blood count • CT, PET, and MRI scans to detect brain volume and activity • Confirmed by autopsy • Tau and β-amyloid test? • Other developed tests have been unsuccessful
Risk Factors • Genetics • Apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) • Deletions in gene coding for α-macroglobulin (serum protease inhibitor) • LDL gene? • Type II Diabetes • Down Syndrome • High cholesterol levels • Stroke and previous head injuries • Tobacco • High homocysteine concentration in blood
Types • Familial Alzheimer’s Disease • Caused by a genetic mutation • All are early onset (younger than 60 years) • Accounts for 10% of the cases • Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease • Most common (90% of the cases) • Typically occurs after age 65
Familial Autosomal AD • Older patients of Down’s syndrome also have neurofirillary tangles and senile plaques 1 1 Martin, Joseph, N Engl J Med
Hypotheses • Amyloid hypothesis • β-amyloid protein • tau hypothesis • tau protein http://www.alzheimers.org/rmedia/mediaroom.htm#animation
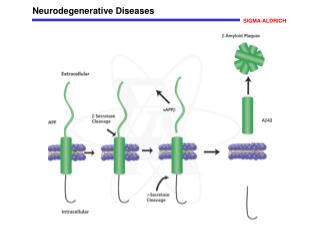
Senile Plaques • Appear first in the cerebral cortex • Results from improper cleavage of APP • Made by β-amyloid, tau, ubiquitin, α-antichymotrypsin, apolipoprotein E, presenilins 1 and 2, α-macroglobulin • β-amyloid fragment (39 – 43 a.a.) is “sticky” and aggregates • Forms intracellularly and transported outside of the neuron http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=12525689
Senile Plaques • Activates de immune system • Disrupts neuron communication and inflammation • β-amyloid facilitates Ca+2 entry to neurons • Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) • Inhibits ubiquitin degradation • Insufficient to cause cell death • High metal concentration APP Copper binding domain
Senile Plaques http://www.alzheimers.org/rmedia/mediaroom.htm#animation
Senile Plaques http://www.alzheimers.org/rmedia/mediaroom.htm#animation
Senile Plaques http://www.alzheimers.org/rmedia/mediaroom.htm#animation
Senile Plaques known mutations Martin, Joseph, N Engl J Med
Amyloid Tracer • “Compound B” highlights β-amyloid • Currently under human trials • Developed at the University of Pittsburgh Sweden's Uppsala University University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
PIB Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 October 14; 100(21): 12462–12467.
Presenilin Presenilin 1 mutations Presenilin 2 mutations Martin, Joseph, N Engl J Med
Astrocytes and Microglia Cells • Astrocytes become more numerous and produce prostaglandin mediated inflammation • Microglial cells produce free radicals • Produce InterLeukin-1β (IL-1β) and Tumor Necrosis-α (TNF-α) (inflammatory cytokines) • Induce enzymes like nitric oxide synthetase • Inflammation damages neurons causing neuron death
Neurofibrillary Tangles • Typically begin in the entorhinal cortex • Visualized as paired helical filaments on electron microscopy • tau protein maintains the structural integrity of microtubules within neurons • In AD, tau protein becomes hyperphosporylated • Hyperphosporylated tau binds to each other forming NFTs • Neurons full of NFTs die
Neurofibrillary Tangles http://www.alzheimers.org/rmedia/mediaroom.htm#animation
Neurofibrillary Tangles • NFTs not present in all cases • NFTs kill output neurons mostly: • Cholinergic neurons (Ach) • Large pyramidal neurons • Output neurons in the hippocampus
Apolipoprotein • Protein portion of lipoproteins (LDL, HDL, etc.) that transport cholesterol • Synthesized in the liver, by the brain astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes • Does not cross the Blood Brain Barrier • Important risk factor
Apolipoprotein E • 299aa glycoprotein • Acts as the binding site for LDL receptors • Allows lipids to get into the cell • Major lipoprotein for lipid transport between neurons • cholesterol used for synapse plasticity and repair of damaged neurons • Removes oxidized lipids from the brain • Three common forms (E2, E3, and E4) • Usually secreted after brain damage
Insulin • High insulin concentration stimulates nitric oxide synthetase • Combines nitric oxide with superoxide to produce peroxynitrite • Peroxynitrite causes Tyr nitration • AD patients show high Tyr nitration in both neurons and glial cells
Tobacco • Nicotine in rats produces elevation of Nerve Growth Factor, enhancing Acetylcholine production and release • Nicotine reduces β-amyloid production • Incidence of AD is more than double for smokers compared to non-smokers
Treatments • Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors • NMDA Receptor Antagonists • Memantine (Namenda) • β-secretase (BACE) inhibitor? • Anti-amyloid vaccine? • Detoxification of β-amyloid? • Metal ions reduction (Clioquinol)? • Vitamin E intake
Cholinergic Neurons • Regulate attention, the first stage of learning, and memory • Use acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter • Have more microtubules than other neurons
+H2O + Acetylcholinesterase • Breaks acetylcholine • Promotes aggregation of β-amyloid
AchE Inhibitors Donepezil (Aricept) Tacrine (Cognex) Rivastigmine (Exelon) Acetylcholine Galantamine (Reminyl)
NMDA Receptor Antagonist • Memantine/Auxura/Namenda • Regulates Calcium influx • Replaces Magnesium Ions
Clioquinol • Chelates copper and zinc in vitro • Treatment reversed the deposition of amyloid in the brains of mice with AD • Clioquinol cut amyloid deposits in half over a nine week period with no adverse effects.