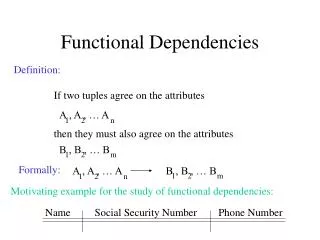
Functional Dependencies
160 likes | 332 Vues
Functional Dependencies. Er . Dharmesh Dubey. Consider the FD set below: F={A->B, C->X, BX->Z} Prove that AC->Z CB->Z AC->Z Proved. (C->X and BX->Z, Pseudo Transitivity). (A->B and CB->Z, Pseudo Transitivity). Consider the FD set below: F={A->B, BC->D}

Functional Dependencies
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Functional Dependencies Er. DharmeshDubey
Consider the FD set below: F={A->B, C->X, BX->Z} Prove that AC->Z CB->Z AC->Z Proved (C->X and BX->Z, Pseudo Transitivity) (A->B and CB->Z, Pseudo Transitivity)
Consider the FD set below: F={A->B, BC->D} Which two are the correct derivation from above FD set? • AC->D • B->D • AD->B • C->AB Answer A: AC->D (Pseudo Transitivity) Answer C: A->B AD->BD (Augmentation) AD->B (Decomposition)
CLOSURE of FD set Consider the FD set below for R(A,B,C,D) F={A->B, A->C, BC->D}, Find F+ A->BC A->D AB->D F+={A->BC, A->D, AB->D} (Union) (Transitivity) (Pseudo Transitivity)
Consider the FD set below for R(A,B,C,D, E, F) F={A->BC,B->E,CD->EF}, F+ are: • {A->BC, A->D, AB->D} • {A->C,AD->CD,AD->EF,AD->F} • {AB-A,C->B,SD->EF} • {A->C,AD->CD,AD->EF} Answer B: A->BC A->B, A->C AD->CD AD->EF
CLOSURE OF ATTRIBUTE Consider the FD set below for R(A,B,C,D,E) F={AB->C,A->D,D->E,AC->B}, Find (AB)+ X={AB} AB->C X={ABC} A->D X={ABCD} D->E X={ABCDE} AC-> B is already in X (AB)+={ABCDE}
Consider the FD set below for R(A,B,C,D,E,F) F={A->BC, E->CF, B->E, CD->EF}, the (AB)+ is: • {ABCEF} • {ABDEF} • {ABCDF} • {ACEF} Answer: A X={AB} X={ABC} A->BC X={ABCE} B->E X={ABCEF} E->CF
Membership Consider R(A,B,C,D,E,F,H) and FD set below, F{A->B,BC->D,D->E,F->DE,DE->H}. Find whether BC->H is the member of given FDs. X=BC X=BCD (BC->D) X=BCDE (D->E) X=BCDEH (DE->H) H is the subset of X, BC->H is a member of F
Consider R(X,Y,Z,W) and FD set below, F={X->YW, XW->Z, Z->Y, XY->Z}. XY-> Z is the member of F. • TRUE • FALSE Answer: A S=XY S=XYW (X->YW) S=XYWZ (XW->Z) Z is the subset of S, XY->Z is the member of F
Nonredundant Cover/Minimal Cover R(A,B,C,D) and F={A->B, B->C, BC->D, DA->B} Find minimal cover. A->B, {B->C, BC->D, DA->B} X={A} B->C, {A->B, BC->D, DA->B} X={B} BC->D, {A->B, B->C, DA->B} X={BC} DA->B, {A->B, B->C, BC->D} X={DA} X={DAB} (A->B) X={DABC} (B->C) Minimal cover is {A->B, B->C, BC->D}
Answer: C A->BC, {CD->E, E->C, D->AEH, ABH->BD, DH->BC} X={A} CD->E, {A->BC, E->C, D->AEH, ABH->BD, DH->BC} X={CD} X={CDAEH} X={CDAEHB} E->C, {A->BC, CD->E, D->AEH, ABH->BD, DH->BC} X={E} D->AEH, A->BC, CD->E, E->C, ABH->BD, DH->BC} X={AEH} ABH->BD, {A->BC, CD->E, E->C, D->AEH, DH->BC} X={ABH} X={ABHC} DH->BC, {A->BC, CD->E, E->C, D->AEH, ABH->BD} X={DH} X={DHAE} X={DHAEBC} {A->BC, CD->E, E->C, D->AEH, ABH->BD} R(A,B,C,D,E,H) and FD F={A->BC, CD->E, E->C, D->AEH, ABH->BD, DH->BC}, the minimal cover is: • {A->B, B->C, BC->D} • {A->B,BC->D,D->E, DE->H} • {A->BC, E->C, D->AEH, ABH->BD} • {A->BC,B->E,CD->EH }
Canonical Cover R(A,B,C,D,E,F) and F={ABD->AC, C->BE, AD-BF, B->E}, Find Fc Apply Decomposition H={ABD->A, ABD->C, C->B, C->E, AD->B, AD->F, B->E} ABD->A,{ABD->C, C->B, C->E, AD->B, AD->F, B->E} (ABD)+={ABDC}, contains A, so remove. H={ABD->C, C->B, C->E, AD->B, AD->F, B->E} ABD->C, {C->B, C->E, AD->B, AD->F, B->E} (ABD)+={ABDFE}, no C, so needed. C->B, {ABD->C, C->E, AD->B, AD->F, B->E} C+={CE}, no B, so needed C->E,{ABD->C, C->B, AD->B, AD->F, B->E} C+={CBE}, contains E, so remove H={ABD->C, C->B, AD->B, AD->F, B->E} Remove LHS attribute Drop A J={BD->C, C->B, AD->B, AD->F, B->E} (BD)+[H]={BDE} (BD)+[J]={BDEC}, different, don’t drop A. Drop B J={AD->C,C->B,AD->F, B->E} (AD)+[H]={ADBFEC} (AD)+[J]={ADCBFE}, similar, so drop B H={AD->C, C->B, AD->B, AD->F, B->E} Drop D J ={A->C, C->B, AD->B, AD->F, B->E} A+[H]={A} A+[J]={ACBE}, different, don’t drop D AD->B, ={AD->C, C->B,AD->F, B->E} (AD)+={ADCBFE}, contains B, so remove H={AD->C, C->B, AD->F, B->E} AD->F, {AD->C, C->B, AD->B, B->E} (AD)+={ADCBE}, no F, so needed. Fc={AD->C, C->B, AD->B, B->E}
R(A,B,C) and F={A->BC, B->C, A->B, AB->C}, Fcis: • Fc= {A->B, B->C} • Fc= {A->BC, B->C} • Fc= {A->B, B->C,AC->B} • Fc={A->B, B->C,AB->C} R(A,B,C) and F={A->BC, B->C, A->B, AB->C}, Find Fc H={A->B, A->C, B->C, A->B, AB->C} (Singleton) H={A->B, A->C, B->C,AB->C} A->B, {A->C, B->C,AB->C} A+={AC}, no B, so needed. A->C,{ A->B, B->C,AB->C} A+={ABC}, contains C, remove. H={A->B, B->C, AB->C} B->C, {A->B, AB->C} B+={B}, no C, so needed AB->C, {A->B, B->C} (AB)+={ABC}, contains C, remove. Fc= {A->B, B->C}
R(A,B,C) and F={A->BC, B->C, A->B, AB->C}, Find Fc H={A->B, A->C, B->C, A->B, AB->C} (Singleton) H={A->B, A->C, B->C,AB->C} A->B, {A->C, B->C,AB->C} A+={AC}, no B, so needed. A->C,{ A->B, B->C,AB->C} A+={ABC}, contains C, remove. H={A->B, B->C, AB->C} B->C, {A->B, AB->C} B+={B}, no C, so needed AB->C, {A->B, B->C} (AB)+={ABC}, contains C, remove. Fc= {A->B, B->C}
Candidate Key R(A,B,C,D) AND F={AB->C, C->D, D->A}, List candidate keys, prime attributes and non prime attributes. (AB)+={ABCD}, Candidate Key C+={CDA}, Not a Candidate Key D+={DA}, Not a Candidate Key Prime Attributes: A,B,C,D.
Consider R(A,B,C,D,E) and F={A->BC, CD->E,B->D, E->A} Which of the following are the candidate keys for the above relation R ? A EC CD B All are the candidate keys of R