MANAGEMENT OF VUR
580 likes | 1.08k Vues
MANAGEMENT OF VUR. Boris Chertin The Department of Urology Shaare Zedek Medical Centre. Vesicoureteral Reflux. Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), the retrograde flow of urine from the bladder to the upper urinary tract. Vesicoureteral Reflux.

MANAGEMENT OF VUR
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MANAGEMENT OF VUR Boris Chertin The Department of Urology Shaare Zedek Medical Centre
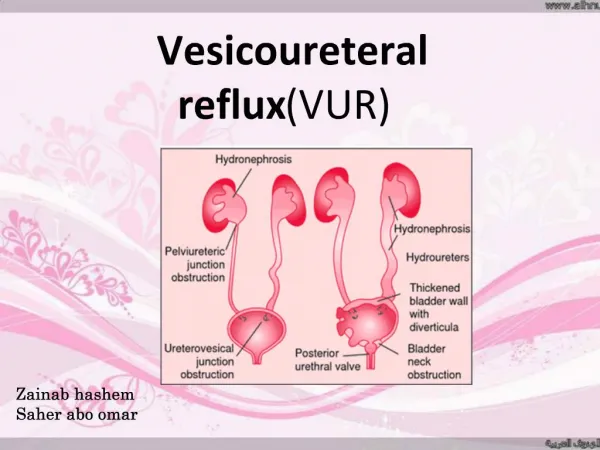
Vesicoureteral Reflux Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), the retrograde flow of urine from the bladder to the upper urinary tract.
Vesicoureteral Reflux In 1883 Semblinow experimentally demonstrated reflux as a normal finding in rabbits and dogs.
The ureter enters the bladder at an oblique angle Adequate posterior support Adequate submucosal length Normal Valve mechanism of the UVJ
EtiologyPrimary reflux (Congenital anomaly of the UVJ) • Abnormal embryologic development of the UVJ unit. • Inadequate posterior support (longitudinal muscle) • Inadequate submucosal length • 5:1 tunnel length to ureteral diameter without VUR Paquin et al, 1957
IncidenceGeneral • Overall - greater than 10% (1% - 18.5%) • Infants with UTI - 70% • Antenatal hydronephrosis - 37% Gender • Female (85%) > male • Infants < 3 months – male (80%) • Whites 10 times > blacks
IncidenceAge Percent decrease likely due to spontaneous resolution with bladder growth and elongation of the ureteral tunnel.
(Bladder obstruction and increased pressure) Anatomic causes Posterior Urethral Valves Ureteroceles (can obstruct bladder neck) Meatal or urethral stenosis Functional causes (more common) Neurogenic bladder Nonneurogenic neurogenic bladder Bladder instability Bladder infections Secondary VUR
Diagnosis Lower urinary tract assessment • Voiding cystourethrography • Nuclear cystography • Ultrasonic cystography
Classification International Reflux Study Committee, 1981
Diagnosis Upper tract assessment • US • Radionuclide imaging (DMSA)
Reflux and the kidney Grade of reflux ~ incidence of nephropathy Skoog et al, 1987
Postinfections scarring Renal scarring can be avoided if infections are prevented Scars and sterile reflux High pressure “water – hammer” Reflux and the kidney Intrarenal reflux
Reflux and the kidney Scars and age • Most severe injury with 1st infection
Reflux of infected urine with interstitial inflammation and damage High grade sterile reflux Abnormal embryological development resulting in renal dysplasia PATHOGENESIS OF RENAL SCARRINGSUMMARY
עקרונות טיפול הכירורגי • יצירת גב תומך לשופכן בקטע תת רירית של כיס השתן • יצירת מהלך שופכן בתת רירית באורך של 2-2.5 ם"מ ( אורך פ' 5 מרוחב השופכן) • עגינת השופכן לקטע נייח של כיס השתן
טיפול כירורגי לשיחזור מערכת שסתום למניעת רפלוקס ניתוח על שםLeadbetter Politano-
טיפול כירורגי לשיחזור מערכת שסתום למניעת רפלוקסניתוח על שם Cohen
תוצאות של השקת שופכנים ניסיון מחלקה אורולוגית שע"צ1979-2003n=328 • 600 שופכנים • גיל 1-17(ממוצא 5.5 שנים) • זכרים 146 • נקבות 182 • דירוג של רפלוקס • דרגה 2 -90 שופכנים (15%) • דרגה 3 180 שופכנים (30%) • דרגה 4 240 שופכנים (40%) • דרגה 5 90 שופכנים (15%)
תוצאות של השקת שופכניםn=600 • רפלוקס תוקן: 95% • הופעת רפלוקס לצד קונטרולטרלי: 3 שופכנים • טיפול אנדוסקופי: 7 שופכנים • טיפול שמרני: 9 שופכנים • כריתת הכליה: 2 ילדים
VURControversy of management Medical versus surgical treatment The rate of spontaneous resolution The rate of infection recurrence The rate of renal damage
International randomized study American arm 131 patients European arm 321 patients 5 years follow up period III & IV Degree reflux Investigation requirements: VCUG & IVP (DMSA)
Medical management European: 151 patients 71% spontaneous resolution 38% recurrent infection American: 41 patients 25% spontaneous resolution Non significant infection rate
Surgical management European: 151 patients Success rate 92% Failure 8% American: 90 patients Success rate 99.4% Failure 0.6%
Birmingham study Total of 104 patients Medical therapy 51 patients, 50% spontaneous resolution. Surgical therapy 53 patients, 98% success rate. Renal scars: No difference.
ARE SIBLING OF PATIENT WITH REFLUX AT MUCH GREATER RISK OF HAVING REFLUX ? • 26% of siblings with VUR in 126 families Dowskin et al , 1976 • 33% of siblings with VUR in 100 families Jerkins and Noe, 1982
TRANSMISSION OF VESICOURETERAL REFLUX • 36 offspring of 23 parents • 24(66%) had VUR • All had higher than Grade II VUR • 4 of the 23 parents underwent nephrectomy due to nonfunctioning kidney • 3 of the 23 parents had renal scars and hypertension Noe et al. J Urol.,148, 1869,1992
ASYMPTOMATIC SIBLINGS • 107 Refluxing patients • 119 Refluxing siblings 64 symptomatic 55 asymptomatic Cascio et al,2002
INCIDENCE OF REFLUX NEPHROPATHY P<0.005 67 % Grade V Grade IV 38 % 36 % 29 %
RISK FACTORS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF RENAL PARENCHYMAL DAMAGE IN FAMILIALVESICOURETERAL REFLUX • HISTORY OF UTI • REFLUX GRADE • AGE AT DIAGNOSIS • ACE DD GENOTYPE ?? Yoneda et al J Urol., 2002
Reflux and the kidney “Reflux Nephropathy” • Focal thinning of renal parenchyma • Calyceal dilatation (clubbed, distorted) • Impaired renal growth with scarring or global atrophy Bailey, 1973
REFLUX NEPHROPATHY AND HYPERTENSION • 10%(5-27) children with renal scar have hypertension • Reflux nephropathy is a commonest cause of severe hypertension in childhood • Increase of the foetal death by 4-5 fold in those who had hypertension at conception
STING - subureteral teflon injection התיקון האנדוסקופי על ידי הזרקת PTFEתואר לראשונה בשנת 1984 על ידי Puri and O'Donnell. זוהי שיטה השונה מהותית מהניתוחים הסטנדרטיים לתיקון הרפלוקס הכליתי.
PTFE - Teflon • נמצא בשימוש נרחב בתחומי הרפואה הניתוחיים. • משחת ה- PTFE הינה תרכובת של חלקיקים אינרטיים מבחינה ביולוגית של PTFE המומסים בגליצרין.
POLYTETRAFLUOROETHYLENE (PTFE)TEFLON • Medical application • Vascular grafts • Heart valves and aortic implants • Hemodialysis shunts • Endoscopic treatment of urinary incontinence
STING • משנת 1984- התיקון האנדוסקופי עם הזרקת טפלון הינה שיטה יעילה אשר הוכחה לאורך השנים. • משנת 1988 מחלקה אורולוגית מרכז רפואי שערי צדק היתה המחלקה הראשונה בארץ והשלישית בעולם אשר החלה בטיפול אנדוסקופי. • אין הסתייגויות לגבי יעילות והנוחות בטיפול האנדוסקופי. • קיימות הסתייגויות לגבי החומר המוזרק באשר לנדידה של חלקיקים מיקרוסקופיים לבלוטות הלשד ואברים מרוחקים אחרים.
TEFLON MIGRATIONAnimal studies • Teflon granuloma formation in the pelvic lymph nodes, lung, kidney, spleen following periurethral Teflon injection ( Malizia et al JAMA 1984, 3277) • Endoscopically injected Teflon into periureteric region was found in the lungs and brains of two dogs (Aaronson and Rames Eur Uro 34(3): 233, 1998)
TEFLON MIGRATIONAnimal studies • No evidence of migration following STING injection • Lung migration following intravenous injection • Intracerebral vessels migration without evidence of brain damage following intracarotid injection Miyakita and Puri J Urol 152, 636, 1994
STINGניסיון מרכז רפואי שערי צדק 1988-2003 • 338 חולים- 603 שופכנים • 69 - זכרים • 269 - נקבות • גילאים בין שנה ל-27שנים (גיל ממוצע 6.9 שנים)
הרפלוקס במערכות המאספות רפלוקס למערכת כפולה דו צדדית 3% רפלוקס למערכת מאספת כפולה חד צדדית 11% רפלוקס דו"צ עם כיס שתן נוירוגני% 2 רפלוקס דו צדדי 44% רפלוקס חד צדדי% 40
STING(1984-1996) • Total number of patients-8332 (1921 boys, 6411 girls) • Age range 2 months-15 years (Mean age 4.5 years)
GRADING OF VUR IN 12251 URETERS ACCORDING TO INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF REFLUX
? • Does PTFE migrate? • Does the disseminated material have any adverse effects? • Does malignant transformation occur?
ALTERNATIVES TO TEFLON • Bovine Collagen • Volume loss • Not suitable for high grade reflux • Silicone • Similar to Teflon • Chondrocytes • Two stage process • Poor long-term effectiveness • Deflux
ENDOSCOPIC TREATMENT OF VUR WITHDEXTRANOMER/HYALURONIC ACID COPOPOLYMER (DEFLUX) • Dextranomer microspheres in 1% hyaluronic solution • Diameter 80-100 µm • 23% volume reduction 12 months after injection ( animal studies)