Array Antennas for Packet Transmission Networks
50 likes | 213 Vues
Array Antennas for Packet Transmission Networks. Antonio Pascual Iserte, Nada Ahmed Awad, Ana I. Pérez-Neira. DEPT. OF SIGNAL THEORY AND COMMUNICATIONS POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY OF CATALONIA (UPC)

Array Antennas for Packet Transmission Networks
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Array Antennas for Packet Transmission Networks Antonio Pascual Iserte, Nada Ahmed Awad, Ana I. Pérez-Neira DEPT. OF SIGNAL THEORY AND COMMUNICATIONS POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY OF CATALONIA (UPC) Communications Signal Processing Group, Barcelona, SPAIN TELECOMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGICAL CENTER OF CATALONIA (CTTC), Barcelona, SPAIN {nahmed,tonip,anuska}@gps.tsc.upc.es Workshop on Broadband Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks and Services, 12th-13th September 2002, ETSI,Sophia Antipolis,France
Ad-hoc networks operate in the unlicensed 2.4GHz ISM band. Different types of Interference sources. Use of spatial diversity schemes to combat interference in a time variant interference scenario. receiver architecture enhanced with the Generalized Sidelobe Canceller (GSLC). Simulations
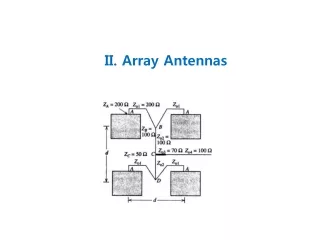
Generalized SideLobe Canceller Signal Model: Array design -“quiescent”: -blocking matrix: -adaptive beamvector: (NLMS)
BER evaluation for (non-)adaptive algorithms (GSLC). PARAMETERS -Angular spread: 15º -IEEE 802.11b interference: mean SIR = -10 dB