RHETORIC RHETORIC RHETORIC
220 likes | 485 Vues
RHETORIC RHETORIC RHETORIC. “The ability, in either case, to see the available means of persuasion.” --Aristotle, Greek philosopher. With a partner:. Pretend one of you is a parent and the other is the child. Child-persuade your “parent” to consider buying you a new smartphone.

RHETORIC RHETORIC RHETORIC
E N D
Presentation Transcript
RHETORICRHETORICRHETORIC “The ability, in either case, to see the available means of persuasion.” --Aristotle, Greek philosopher
With a partner: • Pretend one of you is a parent and the other is the child. • Child-persuade your “parent” to consider buying you a new smartphone. • Parent – after your “child” is done persuading, work with your “child” to write down the methods used to persuade (child should assist you recall, if needed). Which ones were effective? Ineffective? • Were any of the methods/appeals used by the child based on emotion? Based on the child’s character (“I make good grades” etc.)? Based on facts?
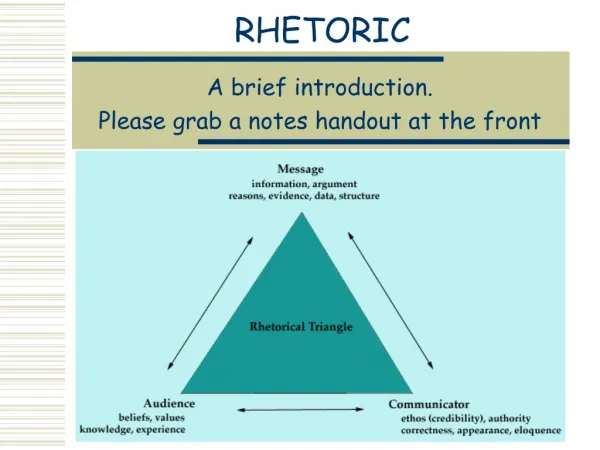
PATHOS • Pathos – probably more easily recognized since it relies on EMOTIONAL appeals. Usually lots of vivid sensory details to awaken the senses and manipulate emotions. • Politicians kissing babies or shaking hands of the elderly • PETA ads • Ally Bank Ad • Volvo Ad • Allstate “Mayhem” Ad
ETHOS • An ethical appeal by focusing on the qualifications of the speaker or character of the speaker. • The credibility of the speaker is supremely important with this appeal. Audiences tend to believe speakers who are intelligent, trustworthy, and honest. The speaker may appeal to principles of religion, patriotism, societal stands, and humanitarism • Examples may include: • Celebrity/expert endorsements • A teen’s argument that he should be allowed to do something because he is responsible. • Shell Oil Company’s print ad, “Cloud the Issue. .. Or Clear the Air?” • U.S. Marines ad • Farmer’s Insurance Ad • Bridgestone Ad
Logos • Uses logic, facts, reasons, statistics, data, and numbers to persuade. • The speaker uses logical appeals, so she will avoid inflammatory language and he will be sure to connect his claim to evidence. • Some examples – test results, research findings, eyewitness testimony, statistics, facts, cause-effect (keep in mind that ads may use “pseudo-scientific” results to sell a product) • L’Oreal Ad (pseudo-scientific) • The Truth PSA
Common Propaganda Devices • Name Calling • Glittering Generalities • Transference • Testimonials • Plain Folks • Snob Appeal • Card Stacking • Bandwagon • Individuality
Name Calling • This device gives bad names to those individuals, groups, nations, races, policies, beliefs, and ideals which the propagandist would have us condemn or reject. • Name-calling causes us to form a judgment without examining the evidence on which it should be based. • Here, the propagandist appeals to our hate and fear.
Glittering Generalities • These words suggest shining ideals. • As name-calling seeks to make us form a judgment or reject, Glittering Generalities seek to make us accept and approve…without examining the evidence. • Beware of words that appeal to your senses in a positive way, thus you trust the message and what it stands for: • Freedom • Loyalty • The American Way • Generosity • Love http://www.visiblemeasures.com/adage Evian- Babies (feeling young)
Transference • This technique can be described as carrying over the authority, sanction, and prestige of something we respect and revere to something the propagandist would have us accept. • Symbols such as the cross, the American flag, or Uncle Sam are often used in transfer ploys. • “If the church or the U.S. approves of it , then you should too.” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FdW1CjbCNxw
Testimonials • This devices is employed to make us accept something by securing statements or endorsements from prominent or famous people. • The point to remember is that no person’s opinion is particularly valuable except for in that person’s field of work. • Tiger Wood’s opinion of a golf club is worth more than his opinion of a razor blade. http://www.visiblemeasures.com/adage Jennifer Lopez- Kohl’s
Plain Folks • The Plain Folks device is used by politicians, business, educators, and even churches to win our confidence by appearing to be common people just like ourselves. • For example, during election time, you will see candidates doing ordinary activities like walking his dog, exercising, or playing with his children. • They want to give the impression of being a regular guy.
Snob Appeal • The opposite of Plain Folk. • Some propagandists want you to have the feeling that only the best, most beautiful, or most elite people will possess or support a particular product or ideal. • Consider ads for Mercedes or Rolex. • Gold Cards • Platinum Cards
Card Stacking • This device is used when the propagandist only wants us to know part of the truth. • They do not tell the whole story to sway opinion. • For example, a car repair shop might say that their technicians have an average of 5 years experience. What they do not tell you is that they have 1 technician with 25 years experience and 4 with none.
Band Wagon • This device is used to make us follow the crowd. • It’s the “everybody’s doing it” so “come along and follow the crowd” ploy. • PEER PRESSURE! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8grf2HEfGEM
Individuality • The opposite of Band Wagon. • Appeals to your desire to be different or celebrate your own style.
Others • Repetition– continued use of a phrase. • Slogan – Use of a catchy phrase or jingle. • Security – Job, families, or lives will be in danger if you don’t support -------. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=thzUR_mq6OY&feature=related • Product Comparison– Compares Product A to Product B. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8TnG7jyfoWI&feature=related • Before and After - Compares before and after results. • Loaded Words– Using words with either positive or negative connotations. • Flexible, courageous, hero, open-minded • Insider, old, rigid, inexperienced
Closing Thoughts • It is okay to buy a product, support a person, or support a group. • Just know the REAL reason why you support that product, person, or group. • Don’t be manipulated and trapped!!
Propaganda Campaign • Cover sheet (MLA Heading, Title, Due date) • CREATE ONE ORIGINAL ADVERTISEMENT • Use a real or fictitious product, place, or person. • Use one or more propaganda devices to convince a target audience to “buy” your product or person. • Include a written explanation of the propaganda device used and the target audience.
Propaganda Campaign • Include: • Type(s) of propaganda device used. • A written explanation of how the propaganda device(s) is used. • Identify the target audience.