Phase Changes
260 likes | 706 Vues
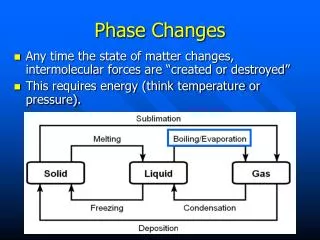
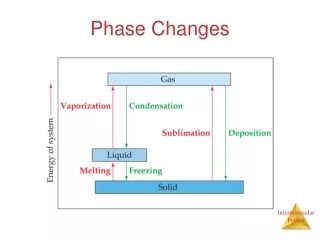
Phase Changes. Any time the state of matter changes, intermolecular forces are “created or destroyed” This requires energy (think temperature or pressure). Phase Changes. Evaporation vs. Boiling Evaporation occurs when particles at the surface of a liquid become a gas.

Phase Changes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Phase Changes • Any time the state of matter changes, intermolecular forces are “created or destroyed” • This requires energy (think temperature or pressure).
Phase Changes • Evaporation vs. Boiling • Evaporation occurs when particles at the surface of a liquid become a gas. [http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/476/488316/Instructor_Resources/Chapter_12/FG12_11.JPG]
Phase Changes • Boiling occurs when particles throughout the liquid become a gas [http://whatscookingamerica.net/Foto4/BoilingWater.bmp]
Boiling causes liquid to gas conversion to occur faster. [http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/602/616516/Media_Assets/Chapter10/Text_Images/FG10_12.JPG]
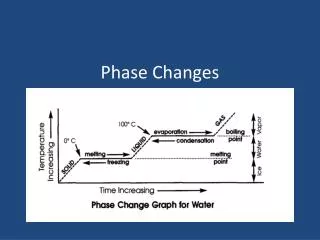
Heating Curve • Graph that shows temperature of a substance over time. • “Plateaus” represent two phases present. Click here for an animation [http://dbhs.wvusd.k12.ca.us/webdocs/NChO/NChO-92-Local-30.GIF]
Heating Curve For H2O or condensing or freezing [http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks3bitesize/science/images/sci_dia_21.gif]
Phase Changes & Thermo • q = (m)(s)(ΔT) • But ΔT = 0 during a phase change • Heat (q) is still being added so a different equation is needed….
Phase Changes & Thermo • q = (moles of substance)(ΔHphase change) • How much energy does it take to change 54.0 g of ice to liquid water?
Phase Changes & Thermo • First, find the moles of water: 54.0 g H2O 1 mol H2O = 3.00 mol H2O 18.0 g H2O
Phase Changes & Thermo • Then, plug into the equation to solve: • q = (3.00 moles)(6.01 kJ/mol) • q = 18.0 kJ of energy
Phase Changes & Thermo • What if the temperature changes and the phase changes? • Example: • How much energy does it take to melt 108 g of ice an heat it to a temperature of 50.0oC?
Phase Changes & Thermo q = (moles)(ΔHfus) + (m)(s)(ΔT) Find the moles of water… 108 g H2O 1 mol H2O = 6.00 mol H2O 18.0 g H2O
Phase Changes & Thermo • q = 36.1 kJ + 22600 J • Or… • q = 58.7 kJ
Phase Diagrams • Graph that shows how pressure and temperature affect the phases of matter. [http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/hillchem3/medialib/media_portfolio/text_images/CH11/FG11_10.JPG]
[http://library.thinkquest.org/C006669/media/Chem/img/Graphs/Phase.gif][http://library.thinkquest.org/C006669/media/Chem/img/Graphs/Phase.gif]
[http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/hillchem3/medialib/media_portfolio/text_images/CH11/FG11_06.JPG][http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/hillchem3/medialib/media_portfolio/text_images/CH11/FG11_06.JPG]
Phase Diagrams • The triple point is where all three phases of matter coexist. Click here for a video example [http://tbn0.google.com/images?q=tbn:tA2QLC4fXbJWjM:http://img.scoop.co.nz/stories/images/0611/0c994da3e92a18f9a4cb.jpeg]
Dry Ice CO2 Gas