Performance
60 likes | 269 Vues
Performance. Performance is about time and the software system’s ability to meet timing requirements. Performance. Event arrival p atterns: Periodic : events arrive predictably at regular time intervals. Stochastic : events arrive according to some probabilistic distribution.

Performance
E N D
Presentation Transcript
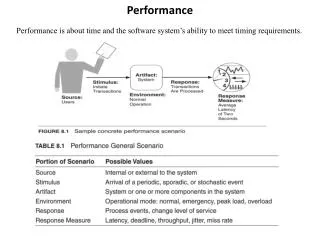
Performance Performance is about time and the software system’s ability to meet timing requirements.
Performance • Event arrival patterns: • Periodic: events arrive predictably at regular time intervals. • Stochastic: events arrive according to some probabilistic distribution. • Sporadic: events arrive according to a pattern that is nether periodic nor stochastic. • Response measures: • Latency: the time between the event arrival and the system’s response. • Deadline: for complete processing • Throughput: number of transactions that the system can process in a unit time • Jitter: allowable variation in latency • Miss rate: the number of events that the system is not able to process • Response time: • Processing time: when the system is working to response by consuming resources • Blocked time: when the system is unable to response, because of resource contention • Contention for resources • Availability of resources • Dependency on other computation
Performance Tactics • Control Resource Demand by reducing the number of events processed • Manage sample rate: reduce the sampling frequency • Limit event response: process events only up to a set maximum rate • Prioritize events: impose a priority scheme that ranks all events according to their importance for services • Reduce overhead: remove intermediaries to improve latency (conflict with modifiability) • Bound execution times: place a limit on how much execution time is used to response to an event • Increase resource efficiency: improving the algorithms used in critical areas to decrese latency
Performance Tactics • Manage Resources • Increase resources: add additional hardware resources • Introduce concurrency: do parallel processing when possible and not extra overhead • Maintain multiple copies of computations: use multiple/replicated servers • Maintain multiple copies of data: use caching and data replication • Bound queue size: control the maximum number of queued arrivals and the resources used to process the arrivals. Need to deal with overflow. • Schedule resources: understand the characteristics of each resource’s use and choose the scheduling strategy that is compatible with it.