How and Why EarthQuakes Occur
270 likes | 404 Vues
How and Why EarthQuakes Occur. Ch 8 Exam Review. Vocab Questions. Fault San Andreas Fault Epicenter Focus Aftershocks Foreshocks. Fault. A fracture in Earth’s crust where movement has occurred

How and Why EarthQuakes Occur
E N D
Presentation Transcript
How and Why EarthQuakes Occur Ch 8 Exam Review
Vocab Questions • Fault • San Andreas Fault • Epicenter • Focus • Aftershocks • Foreshocks
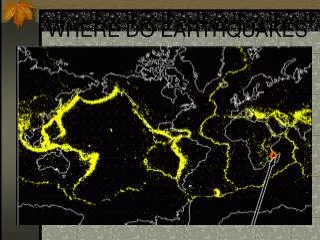
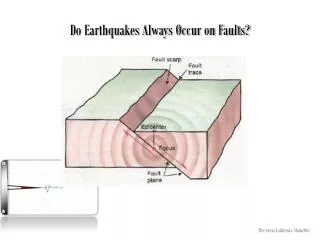
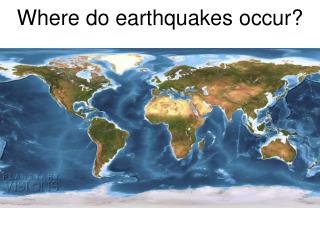
Fault • A fracture in Earth’s crust where movement has occurred • California’s largest fault, the most studied fault because it caused the Great San Francisco Earthquake of 1906 • Focus- inside Earth the source of the energy release/ the place the EQ starts. Energy radiates in all directions • Epicenter-On the surface directly over the focus
Aftershocks • Occuring after and is smaller than the main or largest quake. The get smaller and less frequent over time . Tsunami- ocean wave caused by under sea earthquakes which cause movement of the ocean floor. May travel across entire oceans
foreshocks • Are earthquakes that occur or happen before a major earthquake. • How do we know that shake was a foreshock? • Only if a major shake comes later can we look back and say,”that must have been a foreshock”
More Vocab • Seismogram- the recording on paper or in a computer that is the record of the seismic waves • Seismograph- the device or machine that records the earthquake or seismic waves
Waves • Body waves- • Surface waves- MOST DESTRUCTIVE • 2 types of Body waves are: P-waves and S-waves • P=primary or 1st waves. They travel faster • Travel through solids and liquids • S=secondary or slower waves. They travel slower. Travel only through solids
Because P-waves travel faster • Than S-waves we can use this to determine how far away an earthquake occurred
P and S waves travel at different speeds, the greater the distance from the source, the greater the distance between arrival times.
Travel time curve is used to • Is used to plot the distance from the epicenter to the seismic recording station • seismograph
Triangulating the epicenter • Using 3 different seismograph stations we can find the epicenter
P-waves are faster and generated by compression or back and forth movement
S-waves are slower. They are generated by the up-down or “shear” movement
Elastic Rebound Theory • Or elastic rebound hypothesis is the term used to explain the whole process of how the earth quakes or makes earthquakes
Scales used to measure EQs • Richter- came 1stmeaseured amplitude of largest wave • Moment Magnitude- Most widely used today by scientists. Measure total energy released • Mercalli- Modified Mercalli Scale. measures only intensity of shaking at a given place. Only used for special needs of agencies or by the general public
Liquifaction • EQ Waves cause wet loose ground to compress, raising water pressure in the soil. and soil looses its strength buildings collapse, pancake
Layers of Earth • Lithosphere- crust and upper mantle • Crust • How do we know about the layers inside Earth?
Core • Inner core soild iron and nickle very hot • Solid because of incredible confining pressure • Outer core-liquid iron and nickle • Liquid because of great heat • evide
Continental crust • Granite granitic • Oceanic crust is basalt or basaltic
Evidence of earths layerd structure • Comes from studying earthquake waves