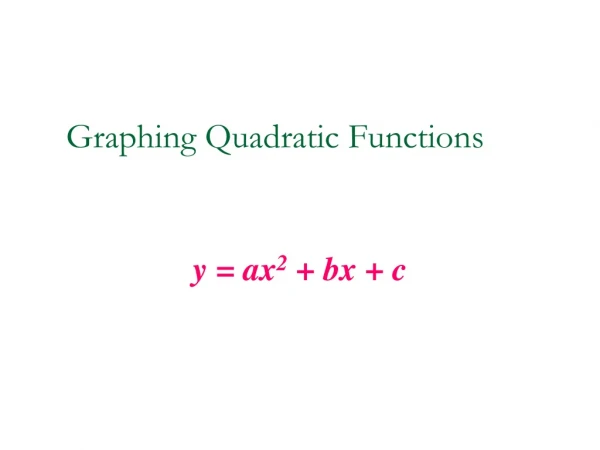
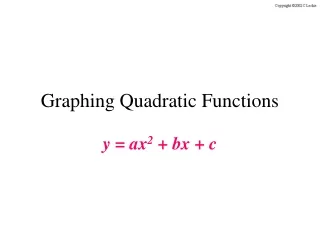
9.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions
220 likes | 258 Vues
Learn about graphing quadratic functions, axis of symmetry, vertex forms, intercept forms, and how to convert between different forms. Practice problems included.

9.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
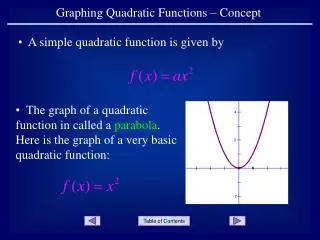
Quadratic Function • A function of the form y=ax2+bx+c where a≠0 making a u-shaped graph called a parabola. - If a is positive, u opens up - If a is negative, u opens down
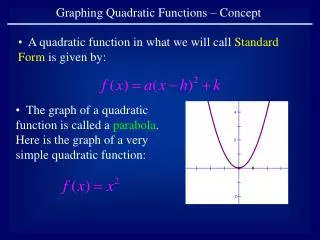
Vertex: • The lowest point (minimum) or highest point (maximum) of a parabola Axis of symmetry: • The vertical line through the vertex of the parabola. Vertex • Axis of • Symmetry
Ex 1: Vertex: Axis of symmetry: Domain: Range:
Steps for Graphing • Find the Axis of Symmetry. (the vertical line x= ) • Find the Vertex • the x-coordinate of the vertex is • plug x-coordinate into the equation to find y-coordinate • Find the Y-intercept • plug 0 in for x to get y • Yint: (0, c)
Ex 2: y = –x2 + 5x – 2 Axis of symmetry: Vertex: Y-intercept: Domain: Range:
9.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions Homework: pg. 531 - #5, 7, 9, 11, 17 (5 problems)
Vertex Form Equation y=a(x-h)2+k • If a is positive, parabola opens up If a is negative, parabola opens down. • The vertex is the point (h,k). • The axis of symmetry is the vertical line x=h. • Don’t forget about 2 points on either side of the vertex! (5 points total!)
Intercept Form Equation y=a(x-p)(x-q) • The x-intercepts are the points (p,0) and (q,0). • The axis of symmetry is the vertical line x= • The x-coordinate of the vertex is • To find the y-coordinate of the vertex, plug the x-coord. into the equation and solve for y. • If a is positive, parabola opens up If a is negative, parabola opens down.
Example 1: Graph y=2x2-8x+6 • Axis of symmetry is the vertical line x=2 • Table of values for other points: x y • 0 6 • 1 0 • 2 -2 • 3 0 • 4 6 • * Graph! • a=2 Since a is positive the parabola will open up. • Vertex: use b=-8 and a=2 Vertex is: (2,-2) • x=2
Now you try one!y=-x2+x+12* Open up or down?* Vertex?* Axis of symmetry?* Table of values with 5 points?
(.5,12) (-1,10) • (2,10) • (-2,6) • (3,6) • X = .5
Example 2: Graphy=-.5(x+3)2+4 • a is negative (a = -.5), so parabola opens down. • Vertex is (h,k) or (-3,4) • Axis of symmetry is the vertical line x = -3 • Table of values x y -1 2 -2 3.5 -3 4 -4 3.5 -5 2 • Vertex (-3,4) • (-4,3.5) • (-2,3.5) • (-5,2) • (-1,2) • x=-3
Now you try one! y=2(x-1)2+3 • Open up or down? • Vertex? • Axis of symmetry? • Table of values with 5 points?
(-1, 11) • (3,11) • X = 1 • (0,5) • (2,5) • (1,3)
Example 3: Graph y=-(x+2)(x-4) • The axis of symmetry is the vertical line x=1 (from the x-coord. of the vertex) • Since a is negative, parabola opens down. • The x-intercepts are (-2,0) and (4,0) • To find the x-coord. of the vertex, use • To find the y-coord., plug 1 in for x. • Vertex (1,9) • (1,9) • (-2,0) • (4,0) • x=1
Now you try one! y=2(x-3)(x+1) • Open up or down? • X-intercepts? • Vertex? • Axis of symmetry?
x=1 • (-1,0) • (3,0) • (1,-8)
Changing from vertex or intercepts form to standard form • The key is to FOIL! (first, outside, inside, last) • Ex: y=-(x+4)(x-9) Ex: y=3(x-1)2+8 =-(x2-9x+4x-36) =3(x-1)(x-1)+8 =-(x2-5x-36) =3(x2-x-x+1)+8 y=-x2+5x+36 =3(x2-2x+1)+8 =3x2-6x+3+8 y=3x2-6x+11