Poetry Terminology Explained
170 likes | 273 Vues
Dive into the world of poetry with Mrs. Tenney as she presents key terms including alliteration, imagery, metaphor, and more. Enhance your understanding of poetic devices and elevate your literary analysis skills.

Poetry Terminology Explained
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Poetry Terminology Presented by: Mrs. Tenney
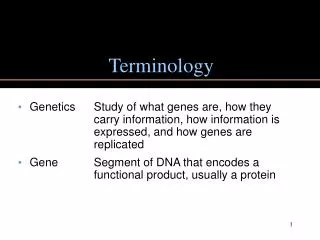
TERMS • Alliteration • Assonance • Hyperbole • Imagery • Irony • Metaphor • Personification • Onomatopoeia • Oxymoron • Repetition • Rhyme • Simile RESOURCES MORE INFO
Meet the Presenter • Mrs. Tenney • 6th year at KAHS • Enjoys reading and writing poetry!
RESOURCES • Academy of American Poets Website • http://www.poets.org/viewmedia.php/prmMID/17105 • Multimedia Resources • http://magnussonllc.wordpress.com/2009/08/10/pimp-my-presentation-alliterations/ • Microsoft Office Clipart Galley
ALLITERATION • Repetition of the same, initial consonant sounds • EXAMPLES: Soft Sighing of the Sea
ASSONANCE • The repetition of the vowel sounds followed by different consonants in two or more stressed syllables. • EXAMPLE: As high as a kite in a bright sky
HYPERBOLE • A bold, deliberate overstatement not intended to be taken seriously. The purpose is to emphasize the truth of the statement. • EXAMPLES: He weighs a ton, I could eat a horse
IMAGERY • Usually these words or phrases create a picture in the reader’s mind. Some imagery appeals to the other four senses (hearing, touch, taste, smell). • EXAMPLES: • Sight – smoke mysteriously puffed our from his ears • Sound – he could hear a faint but distant thump • Touch – the burlap wall covering scraped his skin • Taste – a salty tear ran down his cheek • Smell – the scent of cinnamon floated into his nostrils
IRONY • The general name given to the literary techniques that involve differences between appearance and reality, expectations and result, or meaning and intention. • EXAMPLE: • It was ironic that the police station was robbed. • It was ironic that the Olympic swimmer drowned in the bathtub. • It was ironic that the soldier survived the war and then was shot on his own front porch after returning home safely.
METAPHOR • A figure of speech in which one thing is spoken as though it were something else, a direct comparison of two unlike things. • EXAMPLE: It is raining cats and dogs
PERSONIFICATION • Figurative language in which a nonhuman subject is given human characteristics • EXAMPLE: The wind spoke her name
ONOMATOPOEIA • The use of words that imitate sounds. • Buzz, Thud, Hiss, Woof, Quack
OXYMORON • The junction of words which, at first view, seem to be contradictory, but surprisingly this contradictions expresses a truth or dramatic effect. • EXAMPLES: Pretty ugly, Icy hot
REPETITION • The use, more than once, of any element of language – a sound, a word, a phrase, a clause, or a sentence. • EXAMPLE: By Edgar Allan Poe By the sinking or the swelling in the anger of the bells Of the bells Of the bells, bells, bells, bells
RHYME • Word endings that sounds alike • Internal Rhyme – rhyme within a line • EXAMPLES: Time, Slime, Mime • Internal Rhyme – Scornfully scaly snake which held his very fate
SIMILE • A comparison using like or as. • EXAMPLES: As brave as a lion, As dumb as an ox
MORE INFORMTAION If you’d like to learn more about poetry terms, please refer to Mrs. Tenney’s Moodle page. The website is: http://ecougar.kasd.org/