RNA
230 likes | 429 Vues
RNA. Structure Exon/intron Cap & tail Secondary structure Synthesis Promoter complex Transcription complex Splicing Regulation Promoter elements Enhancer elements Chromatin structure. RNA structure. rRNA-ribosomal tRNA-transfer snRNA-small nuclear miRNA-”micro” regulatory

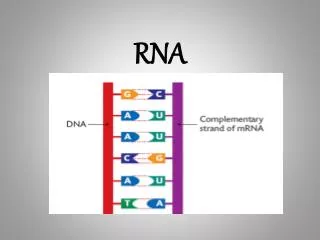
RNA
E N D
Presentation Transcript
RNA • Structure • Exon/intron • Cap & tail • Secondary structure • Synthesis • Promoter complex • Transcription complex • Splicing • Regulation • Promoter elements • Enhancer elements • Chromatin structure
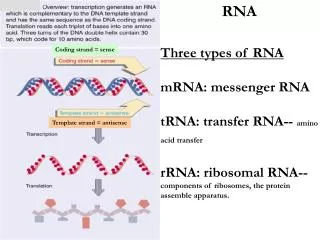
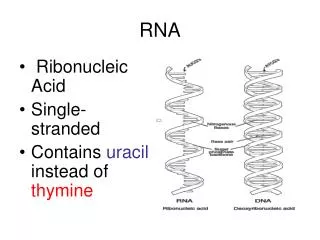
RNA structure • rRNA-ribosomal • tRNA-transfer • snRNA-small nuclear • miRNA-”micro” regulatory • mRNA-messenger • Translated region • 5’ and 3’ untranslated region • Poly-A tail • 7mG cap
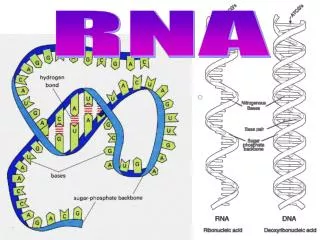
RNA structure • Nucleic acid • Base pairing • Accessory proteins
Promoter Structure Enhancer Core Exon Intron Exon Intron Exon Position -4000 -500 -40-+50 10000+ Gene structure • Promoter/Initiator • Genes are read 5’ to 3’ • TATA box TATAAAA -25 - -30 • Pyrimidine-rich Initator (INR) c/t c/t A n a/t c/t c/t • Gene specific promoter • Intron • Enhancer/repressor • Arrest points • Exon
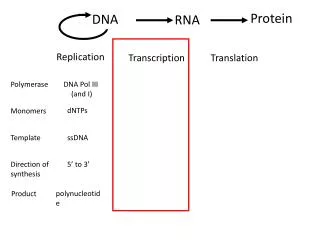
mRNA synthesis and processing • Initiation • Promoter • Enhancer/repressor • Transcription • Elongation • Pause/arrest • Termination • Processing • 5’ cap, 3’ poly-adenylation • Splicing
RNA Transcription • Pre-Initiation Complex (PIC) binds promoter • PIC recruits RNA Polymerase II • PolII transcription elongation complex (TEC) transcribes sequence • 7’-methyl-guanosine cap • Spliceosome ribozymes remove introns • Polyadenylation factors recruit poly-A polymerase
Pre-initiation complex • Transcription Factor IID (TFIID) • TBP TATA box • 11 other subunits • TFIIA • Stability • Blocks repressor proteins • TFIIB • Defines transcription start • Recruits TFIIF/Pol II TFIID TFIIB Inr TATA TFIIA
Pre-Initiation Complex • TFIIE & TFIIH • Helicase • cdk activity • Carboxy-Terminal Domain (CTD) kinase • Phosphorylates S5 Pol II • Start trigger
Pol II • Binds DNA above cleft, melts, and settles on active site • Transcription bubble of ~10bp • Growing RNA exits via saddle • Melted DNA strands exit through clamp RNA Coding Complimentary Clamp DNA Entry Upstream RNA Exit
Active site • Non-specific recruitment “test fit” via PO4 • Template match aligns PolII for catalysis
Transition to Elongation • Early instability • Abortive cycling • Upstream slip • Escape commitment • Mobility of short RNA fragments • Phosphorylation of S2 in CTD • Dissociation of TFII D, A, B
Abortive initiation 3 different bacterial polymerases Full-length product 13nt fragment 9nt fragment 3nt fragment
Critical events • Separation from DNA template: 9nt • Threading the saddle: 15nt • 23 nt complex • Annealing of elongation factors • 5’ capping 1 2 3
Elongation Proper • Pol II is sufficient 200 nt/s • FACT, TFIIF cofactors, 1000 nt/s • TFIIS proofreading
Termination • Pol II transcribes past poly-A signal (AAUAAA) • Recruitment of polyadenylation factors • Poly-A polymerase remains associated w/TEC • Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) binds AAUAAA • Dissociation from DNA requires • PAD-associated P-TEF dissociation • Pol II CTD S2 dephosphorylation • Dissociation of PAF & TFIIS
RNA Processing • Raw transcript “heterogeneous nuclear RNA” • 7’methyl guanine Cap • Capping enzymes part of PIC • 5’ base is backwards • Stability • Translational efficiency 5’-5’ linkage 7’ methylated guanine (methylated after linkage)
Nuclear Structure & Transcription • Nucleolus • Cajal bodies • Transcriptosome/B-Snurposome/Speckle Handwerger & Gall 2006
Splicing • Sequence specific • 5’-AG|GUAAGU… • A(Py)20CAG|G-3’ • Loop/lariat formation • 2’ trans-esterification forms lariat • Only RNA nucleotides have 2’ hydroxyls • 3’ transesterification excises intron • Spliceosome is part of TEC Base OPO3 C O C C C C OH PO4 Base C O C C C C OH PO4 Base C Base O C C C O C C C C PO4 C OH C PO4 PO6
Spliceosome • U1 associates with TEC • Recognizes 5’ splice sequence • U2 is recruited to nascent intron • Recognizes branch point • U4/U5/U6 is recruited • U4 chaperone • U6 forms loop • U5 binds exon ends
Spliceosome • Specificity from spliceosome RNA base pairing • Splice definition prior to termination, but not always excised immediately • Alternative splicing
Nuclear Export • Analogous to protein export (but no ranGTP) • Nuclear eXport Factor targets mRNP • Exon-exon junction complex • Only processed RNA • Transport through Nuclear Pore Complex (Protein export model)
Degradation • 3’ de-adenylation • Crc4p/Pop2p • Exosome mediated degradation • snRNA/snoRNA/rRNA processing • Decapping • Degradation • Missense • Targeted
Poly(A) Binding Protein • Binds A12-25 • Shield mRNA from degradation • Decapping after poly(A) drops to 10 • Inhibition of deadenylation • Stabilization of 5’cap (eIF4F) • Promote translation • Recruits 40S • Reinitiation