RNA
300 likes | 517 Vues
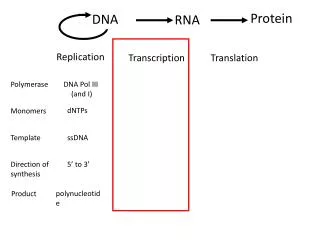
DNA. Protein. RNA. Replication. Transcription. Translation. Polymerase. DNA Pol III (and I). dNTPs. Monomers. Template. ssDNA. Direction of synthesis. 5 ’ to 3’. polynucleotide. Product. DNA. Protein. RNA. Replication. Transcription. Translation. Polymerase.

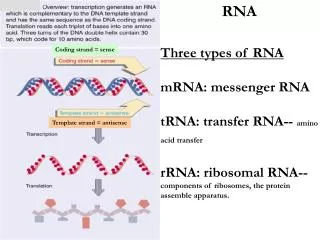
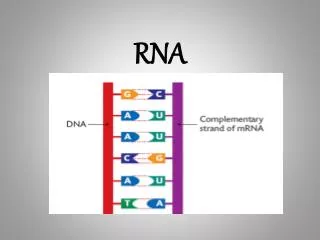
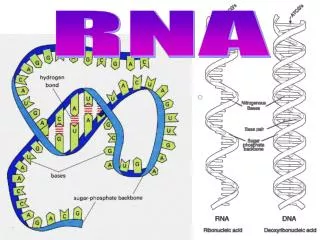
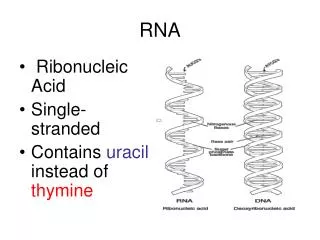
RNA
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DNA Protein RNA Replication Transcription Translation Polymerase DNA Pol III (and I) dNTPs Monomers Template ssDNA Direction of synthesis 5’ to 3’ polynucleotide Product
DNA Protein RNA Replication Transcription Translation Polymerase DNA Pol III (and I) RNA Pol dNTPs NTPs Monomers ssDNA Template ssDNA 5’ to 3’ Direction of synthesis 5’ to 3’ polynucleotide polynucleotide Product
Promoter Transcription unit 5 3 3 5 DNA Start point RNA polymerase Fig. 17-7a-1
Promoter Transcription unit 5 3 3 5 DNA Start point RNA polymerase Initiation 1 5 3 Fig. 17-7a-2 3 5 Template strand of DNA RNA transcript Unwound DNA
Promoter Transcription unit 5 3 3 5 DNA Start point RNA polymerase Initiation 1 5 3 Fig. 17-7a-3 3 5 Template strand of DNA RNA transcript Unwound DNA Elongation 2 Rewound DNA 5 3 3 3 5 5 RNA transcript
Promoter Transcription unit 5 3 3 5 DNA Start point RNA polymerase Initiation 1 5 3 Fig. 17-7a-4 3 5 Template strand of DNA RNA transcript Unwound DNA Elongation 2 Rewound DNA 5 3 3 3 5 5 RNA transcript Termination 3 5 3 3 5 3 5 Completed RNA transcript
Fig. 17-7b Nontemplate strand of DNA Elongation RNA nucleotides RNA polymerase 3' 3' end 5' Direction of transcription (“downstream”) 5' Template strand of DNA Newly made RNA
DNA Protein RNA Replication Transcription Translation Polymerase DNA Pol III (and I) RNA Pol dNTPs NTPs Monomers ssDNA Template ssDNA 5’ to 3’ Direction of synthesis 5’ to 3’ polynucleotide polynucleotide Product
Fig. 17-5 Second mRNA base First mRNA base (5 end of codon) Third mRNA base (3 end of codon)
the mechanism of translation Amino acids Polypeptide tRNA with amino acid attached Ribosome Trp Phe Gly tRNA Anticodon Codons 5 3 mRNA
3 Amino acid attachment site 5 Fig. 17-14 Hydrogen bonds Anticodon (a) Two-dimensional structure Amino acid attachment site 5 3 Hydrogen bonds 3 5 Anticodon Anticodon (c) Symbol used in this book (b) Three-dimensional structure
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (enzyme) Amino acid • Attaching amino acids to tRNAs: • Amino-acyl tRNA synthases • 20 different synthases • Require ATP • Each must be specific to the right amino acid and tRNA(s) P P P Adenosine ATP P Adenosine tRNA P P i Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase P i P i tRNA P Adenosine AMP Computer model Aminoacyl-tRNA (“charged tRNA”)
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthase (ATSGLN) tRNAGLN Adenylated Glutamine
P site (Peptidyl-tRNA binding site) A site (Aminoacyl- tRNA binding site) E site (Exit site) E P A Large subunit mRNA binding site Small subunit Fig. 17-16b (b) Schematic model showing binding sites Growing polypeptide Amino end Next amino acid to be added to polypeptide chain E tRNA mRNA 3 Codons 5 (c) Schematic model with mRNA and tRNA
The Ribosome LSU SSU
Amino end of polypeptide E 3 mRNA P site A site 5 Fig. 17-18-1
Amino end of polypeptide E 3 mRNA P site A site 5 GTP Fig. 17-18-2 GDP E A P
Amino end of polypeptide E 3 mRNA P site A site 5 GTP Fig. 17-18-3 GDP E A P E P A
Peptide bond formation - Transfer of growing chain from tRNA in P site to tRNA in A site
Amino end of polypeptide E 3 mRNA P site A site 5 GTP Fig. 17-18-3 GDP E A P E P A
Amino end of polypeptide E 3 mRNA P site A site Ribosome ready for next aminoacyl tRNA 5 GTP Fig. 17-18-4 GDP E E P A A P GDP GTP E P A
Initiating translation Large ribosomal subunit 3 U 5 C A P site Fig. 17-17 Met Met 5 3 A G U Initiator tRNA GDP GTP E A mRNA 5 5 3 3 Start codon Small ribosomal subunit Translation initiation complex mRNA binding site
Terminating translation Fig. 17-19-1 Release factor 3 5 Stop codon (UAG, UAA, or UGA)
Terminating translation Fig. 17-19-2 Release factor Free polypeptide 3 3 2 GTP 5 5 Stop codon (UAG, UAA, or UGA) 2 GDP
Terminating translation Fig. 17-19-3 Release factor Free polypeptide 5 3 3 3 2 GTP 5 5 Stop codon (UAG, UAA, or UGA) 2 GDP
Completed polypeptide Growing polypeptides Incoming ribosomal subunits Polyribosome Fig. 17-20 Start of mRNA (5 end) End of mRNA (3 end) (a) Ribosomes mRNA (b) 0.1 µm
RNA polymerase DNA mRNA In bacteria: Translation can happen while transcription is still ocurring Polyribosome Fig. 17-24 0.25 µm Direction of transcription RNA polymerase DNA Polyribosome Polypeptide (amino end) Ribosome mRNA (5 end)
Fig. 18-3a In bacteria: Many genes are organized in operons Operon = group of genes sharing one promoter, expressed as 1 mRNAs containing multiple ORFs trp operon Promoter Genes of operon trpD trpE trpC trpB trpA Stop codon Start codon mRNA 5 B A D C E Polypeptide subunits that make up enzymes for tryptophan synthesis
DNA Protein RNA Replication Transcription Translation Polymerase ribosome DNA Pol III (and I) RNA Pol Aminoacyl-tRNAs dNTPs NTPs Monomers ssDNA mRNA Template ssDNA 5’ to 3’ Direction of synthesis 5’ to 3’ N to C polynucleotide polynucleotide Product polypeptide