Cellular Respiration
130 likes | 303 Vues
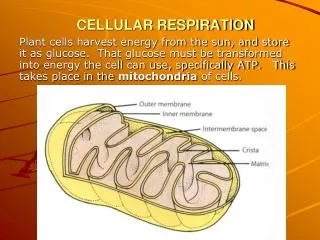
Cellular respiration is a vital process in which food (sugar) is broken down to produce ATP, the energy-storing molecule. Occurring in the mitochondria, this process requires glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2) as reactants. The outputs include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and ATP. The process unfolds in three main steps: Glycolysis, where sugar is broken down; Kreb’s Cycle, which further degrades sugar and releases CO2; and the Electron Transport Chain, where oxygen is used to produce ATP and water. Understanding these steps highlights the importance of cellular respiration in energy production.

Cellular Respiration
E N D
Presentation Transcript
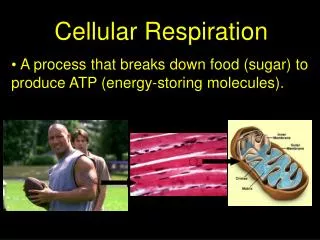
Cellular Respiration • A process that breaks down food (sugar) to produce ATP (energy-storing molecules).
Reactants (what goes in) • Glucose or sugar (C6H12O2) • Oxygen (O2) Products (what comes out) • Water (H2O) • Carbon dioxide (CO2) • Energy (ATP)
What goes into cellular respiration? 2. Oxygen (O2) Glucose (sugar) (C6H12O6)
1. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) 2. Water (H2O) 3. Energy What is made in cellular respiration?
Formula for Cellular Respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
Step 1: Glycolysis Sugar is broken down.
Step2: Kreb’s Cycle or Citric Acid Cycle • We continue to breakdown the sugar. • Carbon dioxide is released.
Step 3: Electron Transport Chain • Oxygen is used and water is also made as a byproduct. • This is where we make all of our energy storing molecules called ATP.
Cellular Respiration Review What is this? • Needs • 1. Glucose (sugar) • 2. Oxygen (6) • Makes (Produces) • 1. Carbon Dioxide (6) • 2. Water (6) • 3. Energy Mitochondria