Stakeholder Objectives
410 likes | 804 Vues
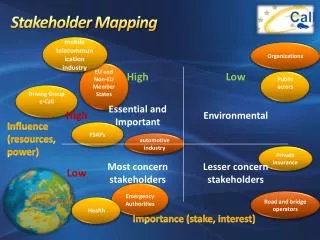
Stakeholder Objectives. Summary of Stakeholder Objectives. Stakeholder Objectives (based on their needs / expectations, might include:. Stakeholder. Objectives. Wealth, profits, growth, reputation. Owner. Capital gain on shares; regular, secure / high dividends; a say in the business.

Stakeholder Objectives
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Summary of Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives (based on their needs / expectations, might include: Stakeholder Objectives Wealth, profits, growth, reputation. Owner Capital gain on shares; regular, secure / high dividends; a say in the business. Shareholder
Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives Job security, status, personal power, high rewards; organisational profitability / growth; lack of interference in decisions. Directors & Managers
Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives Employees High / fair play, interesting work, job security, promotion, training opportunities, safe working environment, fair treatment, a say in decisions.
Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives Customers& Consumers Quality / value for money; functional safe products; clear, accurate product / service information; accessibility to product / service; choice; credit facilities; high standards of customer choice.
Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives Suppliers Secure, regular & profitable contracts; discounts; timely payment; good working relationship; fair terms of trade;organisational growth.
Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives Timely payment, good security. Creditors
Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives Fair and ethical competition. Competitors
Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives Job creation; payment of taxes; compliance with environment, health, safety and environmental legislation. Government
Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives Employment; investment and sponsorship in local events; minimum noise, congestion and pollution. Local Residents
Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives Protection of employee rights, eg fair and equal treatment. Trade Unions
Stakeholder Objectives Stakeholder Objectives Minimisation of waste, pollution; re-cycling and respect for the natural environment; equal opportunities; maintenance of standards and codes of practice. Pressure Groups
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Owners and Shareholders Some insist on corporate responsibility: demand improvements in working conditions, control of emissions, waste; influence decisions over suppliers.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Owners and Shareholders Others: influence business to take most profitable option, (regardless of the effect on society).
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Directors and Managers May have their own agenda eg increased pay, power, status – make business decisions whichhelp achieve these goals, rather than the owner(s).
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Employees Higher expectations: demand better working conditions, better quality of working life, want to be consulted.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Employees Forces business to look for ways of attracting and retaining staff, particularly if high competition for staff, eg by offering:
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Employees • attractive rewards packages • a chance to participate • flexible working arrangements.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Customers / Consumers Generally more educated, experienced – higher expectations, different objectives to previous generations.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Customers / Consumers Force firm to adopt a more customer orientated approach – led to ‘customer care’ departments / policies / charters, plus increased provision of ‘after sales’ services.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Suppliers Want profit and / or organisational growth – timely payment important. May offer discounts – influence a business to ensure payment is made on time.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government Government macro economic objectives include: • Stable economic growth • Low inflation • Low unemployment • A healthy balance of payments.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government General ways these objectives benefit business: • Stable economic growth – greater income to spend on goods / services – greater sales, profits, better cashflow.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government General ways these objectives benefit business: • Stable prices / low inflation – helps ensure workers don’t become concerned about wage levels and forceful about pay increases (above rate of inflation).
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government General ways these objectives benefit business: • Low unemployment – helps keep steady demand for a firm’s products as consumers have a regular income.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government To achieve objectives government use: • Monetary policy:the money supply, rates of interest, exchange rates, amount of credit available, to control the level of spending within the economy.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government Monetary policy: Eg if inflation – the government will increase interest rates to reduce demand.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government To achieve objectives government use: • Fiscal policy:The use of government taxes to control level of consumer spending and business activity
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government Fiscal policy: Eg if low demand (resulting in unemployment) – Govt will lower taxes – people more money to spend.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government To achieve objectives government use: • Exchange rate / trade policy:The price at which one country’s currency is converted into another.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government To achieve objectives government use: Fixed – central bank buys when market pressures are forcing the value down, (and vice versa). Freely floating – central bank does not intervene.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government To achieve objectives government use: • Supply side policies:Those designed to encourage the free working of markets, including labour, capital, land
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government Supply side policy: Eg restricting union activities, reducing unemployment benefit (labour); Ending monopoly controls + restrictive practices (capital).
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government Policies used have a direct and indirect influence eg: • increase in interest rates – may make an investment too costly. • Changes in corporation tax or VAT – impinge on profit, encourage business to reinvest.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Government Policies used have a direct and indirect influence eg: • Government grants and subsidies (supply side policies) – persuade a business to locate in one area over another.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Pressure Groups May force a business to pursue an environmental objective to avoid negative publicity, and subsequent fall in sales.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Overall, the influence the various stakeholders have will depend upon: • the nature of the business’s activities. • its size, type of legal structure.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Overall, the influence the various stakeholders have will depend upon: • the amount of capital invested and position held within the business (where applicable). • government legislation.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Overall, the influence the various stakeholders have will depend upon: • degree of media attention given to a particular stakeholder’s cause.
How Stakeholder Objectives Affect the Behaviour and Decisions of the Firm Businesses who recognise the influence stakeholders can have on their business, especially their image and reputation, and take into account their objectives when setting business objectives / deciding how to meet them, are likely to be the most successful.
2871: Businesses, Their Objectives and Environment - END - OBJECTIVES & STRATEGY Stakeholder Objectives