Understanding Prisms: Shapes, Formulas, and Properties
100 likes | 180 Vues
Learn about prisms: types, lateral area, total area, volume, and key geometric properties such as bases, altitude, lateral faces, and edges. Explore how to identify right prisms and oblique prisms. Find formulas for calculating prism measurements and examples in 3D geometry.

Understanding Prisms: Shapes, Formulas, and Properties
E N D
Presentation Transcript
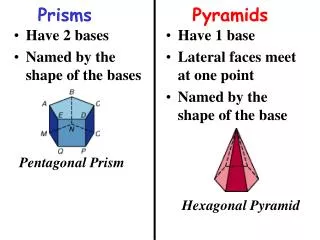
Prism a 3d solid with the following: BASES – congruent polygons in parallel planes ALTITUDE– a segment joining the two bases and to both (length of altitude is the height of the prism) LATERAL FACES – the faces that are not bases (always parallelograms) LATERAL EDGES – the parallel segments joining the lateral faces
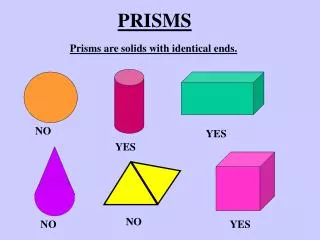
If the lateral faces of a prism are rectangles, then the prism is a right prism. If the lateral faces of a prism are not rectangles, then the prism is oblique. (see pg. 475) Prisms are named by the shape of their bases. Triangular prism, rectangular prism, pentagonal prism.
The LATERAL AREA (LA) of a prism is the sum of the areas of the lateral faces of the prism.The TOTAL AREA (TA) is the sum of all of the prism’s faces (lateral area plus the sum of the bases of the prism). TA=LA +2B
THM 12-1 The Lateral area of a RIGHT prism equals the perimeter of a base times the height of the prism. LA=Ph
THM 12-2 The VOLUME of a RIGHT prism equals the area of a base times the height of the prism. V=Bh
2 2 3 120 u 180 u 120 u LA = TA= V= 4 5 12
2 3 48 u 2 80+4 u 96+12 u LA = TA= V= 60 3 2 4
100 u 132 u 80 u 2 2 3 5 2 8 LA = TA= V=