Early River Valley Civilizations
150 likes | 359 Vues
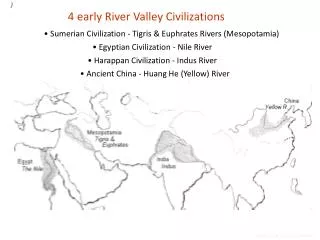
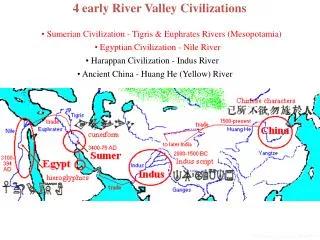
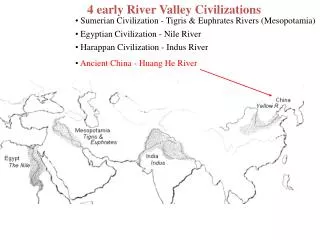
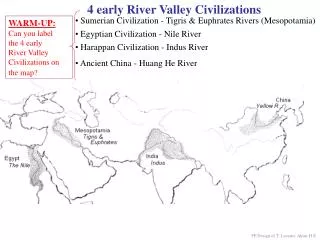
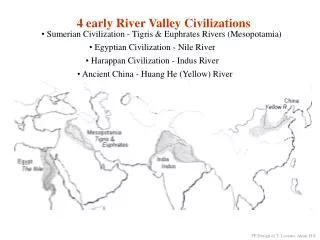
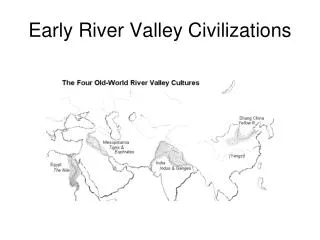
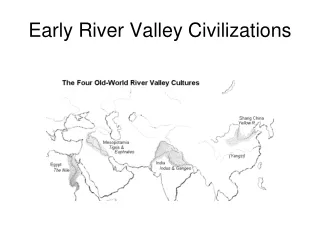
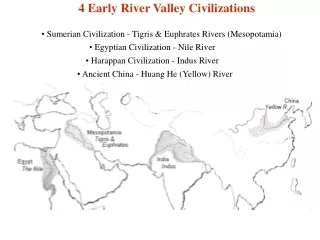
Early River Valley Civilizations. Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, and China 3500 B.C. to 450 B.C. Mesopotamia Fertile Crescent Tigris and Euphrates: “land between the rivers ” Rise of city-states (Ur, Uruk , Kish, Umma ) At first controlled by priests but military leaders soon take over

Early River Valley Civilizations
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Early River Valley Civilizations • Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, and China • 3500 B.C. to 450 B.C. • Mesopotamia • Fertile Crescent • Tigris and Euphrates: “land between the rivers” • Rise of city-states (Ur, Uruk, Kish, Umma) • At first controlled by priests but military leaders soon take over • Military leaders would create a dynasty: series of rulers from single family • More and more city-states increase trade between cities which also increases cultural diffusion: one culture spreading to another
More on Mesopotamia • Religion • Polytheism – belief in many gods • Thought gods controlled nature, behaved like humans but people were servants to gods • Social Classes • Kings and priests at top • Merchants next, slaves at bottom • Women had rights; were priests, merchants, artisans • Sumerian Technology • Invented the wheel, sail, and plow; first to use bronze • Made advances in arithmetic and geometry • Developed arches, columns, ramps, and pyramids • Cunieform • Studied astronomy, chemistry, and medicine
Hammurabi • King of Babylonian Empire (1792-1750) • Babylon was capitol of empire • Hammurabi creates a code of law • 282 laws on all aspects of life; engraved in stone and made public • Set different punishments depending on social class, gender • Goal for government to take responsibility for order, justice
Egypt • Civilization arose along 4,100-mile Nile River • Yearly flooding made land very fertile • Ruled by pharaohs: god-kings, actually viewed them as deities • Was a theocracy: government based on religious authority • Pharaohs controlled every aspect of Egyptian life: religion, government, army • Built the pyramids, elaborate tombs to meet needs after death • Made from huge (2-15 ton) stone blocks, some over 400 feet tall • Mummified before placed in tomb: process that prevents body from decaying
Egyptian life • Social classes • Society shaped like a pyramid, Pharaoh down to farmers and laborers • A few people at the top have all the power, most people at the bottom • Women have many of the same rights as men • Egyptian writing • Hieroglyphics: pictures represent ideas • Writing done on papyrus reeds • Egyptian technology • Invented the current 365 day/12 month calendar • Developed system of written numbers, geometry • Egyptian medicine becomes famous in the ancient world
India – Indus River Valley • Indian subcontinent - landmass that includes India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh • Himalayan Mountains (tallest in world) separate it from rest of Asia • Mountains to north, desert to east, protect Indus Valley from invasion • Rivers and flooding from mountain winter-melt were environmentally important in Mesopotamia and Egypt • In India, monsoons (seasonal winds) dominate the climate • Summer winds blow from Indian Ocean and can bring huge amounts of rain, if rain is low then droughts can occur
Indus Valley Civilization • Larger area than Mesopotamia • Around 2500 B.C. people built cities of brick laid out in grid system • Built on mud-brick platform to protect from floods • Had brick walls for protection • Streets in grid system were 30 feet wide • Cities had plumbing and sewage systems • Called Harappan civilization after capitol city, Harappa • Writing system had 400 symbols but we can’t decipher it now • No big social divisions in culture • Religious artifacts have links to modern Hinduism • Traded with other peoples, including Mesopotamia
China • Natural barriers isolate them from other areas • Ocean, mountains, deserts • Huang He and Yangtze create fertile lands much like Mesopotamia • Geographic isolation means lack of trade • First cities arise around 2000 B.C., built of wood, upper classes live inside city and poorer people live outside, massive walls for military defense
Chinese culture • People view China as center of world, view others as uncivilized • The group is more important than the individual • Family is central social institution with respect for parents a virtue • Elder males control family property • Women expect to obey men, even sons • King and warrior-nobles lead society and own the land • Writing system used symbols to represent syllables, not ideas like heiroglyphics
Chinese government • Dynastic cycle—pattern of the rise and decline of dynasties • Mandate of Heaven - the belief that a just ruler had divine approval, this helps explain dynastic cycle • Feudalism – system where kings give land to nobles in exchange for services • Zhou Dynasty builds roads, canals to improve transportation, used coins to make trade easier