Plate Boundaries and Plate Tectonics
120 likes | 957 Vues
Plate Boundaries and Plate Tectonics. By: Mike Brady, Joe Fassel, Liz Alessi, Brittany Spalding, Josh Minnich. Plate Boundaries. -a fracture that separates one plate from another. 3 different types. Divergent boundary Convergent boundary Transform boundary. Divergent.

Plate Boundaries and Plate Tectonics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
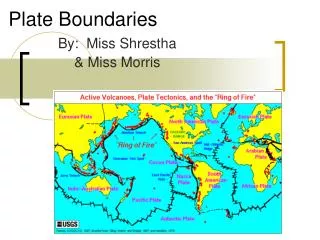
Plate Boundaries and Plate Tectonics By: Mike Brady, Joe Fassel, Liz Alessi, Brittany Spalding, Josh Minnich
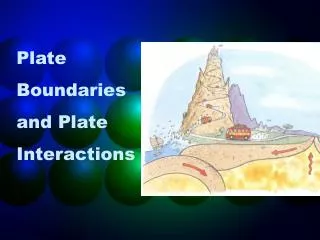
Plate Boundaries -a fracture that separates one plate from another
3 different types • Divergent boundary • Convergent boundary • Transform boundary
Divergent • Forms when two plates move apart from each other, then the underlying asthenosphere oozes upward to fill the gap between the separating plates. Plates Involved: Ocean-Ocean Ex) Mid-Atlantic Ridge Continent- Continent Ex) East African Rift
Convergent • Two lithospheric plates move toward each other, 2 plates of different densities come together and the denser one sinks beneath it. • Plates Involved: Ocean-Ocean Ex) Western Aleutians Ocean-Continent Ex) Andes Continent-Continent Ex) Himalayas
Transform • This forms when two plates slide horizontally past on each other as they move in opposite directions. • Plates Involved: • Ocean-Ocean Ex) East Pacific Rise • Continent-Continent Ex) San Andreas fault
Short Term Climate Change • Climate change can occur rapidly in a few ways due to plate tectonics. • Plate tectonics can cause waterways to close or mountains to form. • This can cause changes in air currents and water currents, which in turn causes climate changes.
Long Term Climate Change • Plate Tectonics can cause extreme changes in climate over a geologically long period of time. • This occurs when a continent shifts far distances and therefore changes its latitude relative to the equator and the poles.
Sea Floor Spreading • Sea floor spreading causes the global climate to change in two ways. • When the sea floor spreads slowly the Mid-Ocean ridge system is relatively narrow. • This displaces a relatively small amount of water, and exposes a large amount of marine limestone which, during the process of weathering decreases the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere, and decreases the global temperature.
Sea Floor Spreading Cont. • When the sea floor spreads rapidly the Mid Ocean Ridge system is wider, and displaces a larger amount of water. • This raises sea level and in turn cuts down the amount of exposed marine limestone. • Which in turn reduces the amount of CO2 removed through weathering, and increases the global temperature.
Affect of More Lands and at Higher Latitudes • Alter ocean currents and therefore heat transport • Alter global atmospheric circulation • More glaciers over land, higher albedo, cooler temps
Sources • http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter18/plate_tech.html • Thompson & Turk, Earth Science and the Environment,3rd Edition.