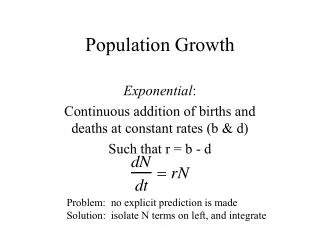
Population Growth
300 likes | 831 Vues
Population Growth. A high life expectancy indicates a higher standard of living Canada = 82.2 years (Ranked #12 in world) USA = 79.3 (Ranked # 31 st ). Life Expectancy. Hans Rosling 200 countries video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jbkSRLYSojo. Lowest life expectancy

Population Growth
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A high life expectancy indicates a higher standard of living • Canada = 82.2 years (Ranked #12 in world) • USA = 79.3 (Ranked # 31st) Life Expectancy
Hans Rosling 200 countries video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jbkSRLYSojo Lowest life expectancy 183) Sierra Leone, 50.1 182) Angola, 52.4 181) Central African Rep., 52.5 180) Chad, 53.1 179) Cote d’Ivoire, 53.3 Highest life expectancy 1) Japan, 83.7 2) Switzerland, 83.4 3) Singapore, 83.1 4) Australia, 82.8 5) Spain, 82.8
Dependency Load • Everyone younger than 15 and older than 65 • They are most likely to be socially as well as economically dependent on working-age people With such a huge dependency load, what kind of jobs will be in demand in the near future?
Global Population Growth • The 8 billionth person will be born in 2024 • Every day 233,000 more people are added to the world • All these people need to be fed and clothed and housed • It took thousands of years to reach 1 billion people (1800) • The world went from 6 billion to 7 billion in just 12 years • Growth Rate: • Africa 2.5% • Asia 1.1% • Europe 0% • Latin America 1.2% • North America 0.4% • Oceania 1.1% • Africa’s doubling time is 27 years • India will have the largest population (1.5 billion) by 2030
High Growth Rate = why is it a bad thing • You don’t want to have a very high Birth Rate; that means your population is growing too quickly • That means you have too many children and not enough older people • Leads to overcrowding and resource competition • There is a correlation with lower education, more poverty, lower quality of life • What countries are growing the fastest? • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3nnbd1b_tKQ 3:50
Rapid shrinking of the workforce could have a negative impact on an economy • When the population gets smaller, society becomes less dynamic and competitive • Fewer people paying into pension funds at the same time that more and more old people are drawing from them (and living longer and longer thanks to modern medicine). • Where is the population shrinking the fastest? • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qn9DDsxfpCA 4:19 Negative Growth Rate – why is it a bad thing?
Is there an Optimal Pyramid shape? • The top will always be smaller than the rest • But the rest is in balance; there are no weird bumps or bulges • Many demographers believe that the world population will stabilize like this at around 11 billion people
Canadian Provinces • Look at the differences between the provinces and territories! • Nunavut has a higher birth rate and death rate than the rest of Canada • http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2011/dp-pd/pyramid-pyramide/his/index-eng.cfm
Living Conditions in Nunavut • It is difficult to eat healthy – look at the insanely high prices of food! • The food costs so much because it all has to be flown in and so it has to cover the transportation costs • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R6opLph6Hr8
What would you do? • Imagine you are the President of a country that has a problem you want to help solve. In either case, list some possible programs/solutions . • Country A: Very high birth rate. Women are having many babies and large families. • Country B: Very low birth rate. Women are having very few babies.
Falling Birth Rate - Singapore • Singapore has a very low birth rate, so the Singaporean government partnered with Mentos to create this “National Night” campaign • It was to encourage couples to make a baby that night • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8jxU89x78ac • Apologies in advance, this song MAY get stuck in your head all day
Falling Birth Rate - Denmark • They also have a very low birth rate • The present rate of 1.7 children per family is not enough to maintain the population • They launched a “Do It For Denmark” campaign to raise fertility • It was an advertising campaign designed to increase the birth rate of the nation launched by a Danish travel agency • Following the implementation of the campaign in 2014, the Danish birth rate increased • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vrO3TfJc9Qw
Incentives to encourage South Koreans to have more babies • lower university tuition fees • state-run child care • cash vouchers • In 2010 ‘Family Day’ was established which required all offices to close at 7 pm and in that way pushing people to spend more time with their families. Falling birth rate – South Korea
The low birth rate in Russia motivated the government to launch the ‘have a baby and win a Fridge’ campaign. • September 12 was declared ‘the Day of Conception’ and all women that would give birth 9 months after would win a fridge, money or even cars Low Birth Rate - Russia
Japan has a catastrophically low birth rate • Japan's population had shrunk by almost 1 million people in 5 years. • By the end of the century, Japan might lose 34 % of its population Shrinking population - Japan
Japan – so many old people • Today, over 25% of Japan's 127 million people are over 65. • By 2055, it's estimated to be 40%. • This will create a ton of healthcare costs.
Extreme Work culture • Japan's extreme work culture, where employees are expected to work into the night, go out drinking with their colleagues, and potentially move across Japan or abroad to advance their careers • The lifestyle of the “salaryman” • No time or energy left to date
Working women • 70% of Japanese women give up work as soon as they have their first child • Japanese men don’t help with the children as much • Not enough daycares • Moms that do go back to work are often vilified and looked down on • Married women are often passed over for promotions since it is assumed they will get pregnant and leave
Young people not dating • 61% of unmarried men and 49% of women aged 18-34 were not in any kind of romantic relationship, a rise of almost 10% from five years earlier. • 45% of women aged 16-24 "were not interested in or despised sexual contact". More than a quarter of men felt the same way • Some resort to virtual reality girlfriends
pensions • Now older people can get pensions when they retire, so they don’t have to rely on children to care for them when they are elderly
A Train Stop for a single person • A train in Hokkaido, Japan stops twice a day for a single passenger – a high school student on her way to school • The station was slated to close in 2012 due to its remote location • The train schedule is based on the girl’s timetable, and so passes by the station on her holidays • That’s how much the population has shrunk in some areas
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ioqic5TYM8k 3.46 Japan's Population Decline: Incredible Facts About Japan's Aging Population • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P5Pwn6JX4eY How Japan’s Economy is Ruining Its Youth • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L1kFik1BZRo 16.40 Japan's Baby Drain