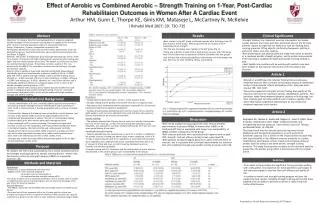
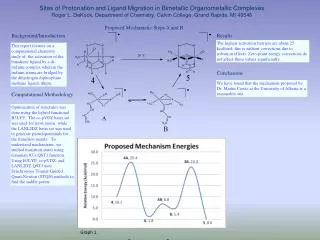
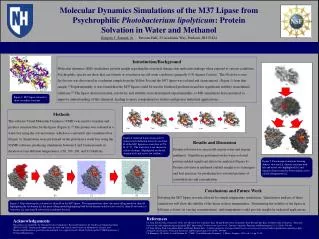
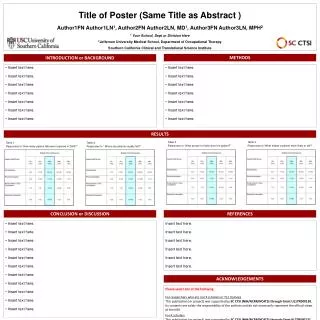
Arabidopsis Thaliana: Model Plant Development & Advantages
240 likes | 350 Vues
Explore the detailed stages of seed and embryo development in Arabidopsis Thaliana, a model plant species. Learn why this plant is favored in research due to its fast growth, small genome, and easy manipulation, with insights from experts.

Arabidopsis Thaliana: Model Plant Development & Advantages
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Background Introduction By Bensen Fan Kristin Gill Maria Garcia
Part I. Seed Development By Bensen Fan
Seed Anatomy Axis Cotyledon
Flower Anatomy Anthers (Makes Pollens) Stigma Ovary (Contains ovules) Pistil
Pollination & Fertilization: Forming of a New Life! Pollen Tube Sperms
Embryo Development: Zygote - Young Embryo Apical Cell Embryo Proper Suspensor Basal Cell Asymmetric Division Terminally Differentiated
Late Development: Torpedo - Mature Embryo SM = Shoot Meristem; RM = Root Meristem
Final Stage: Dormancy Mature Seeds Dormant Seeds
Part II. Arabidopsis thaliana Embryo Development By Kristin Grill
What happens during embryo development? Each stage is essential for embryo development! EMBRYO SAC GLOBULAR HEART TORPEDO MATURATION
Embryo Proper Suspensor Globular Embryo Embryos develop after double fertilization Early embryos consist of 2 regions: 1. Embryo Proper 2. Suspensor
Apical cell Embryo Proper Central Cell Synergids Suspensor Egg Cell Basal cell Embryo Sac 2-Cell Embryo Globular Embryo Early embryo development is a very coordinated developmental process
Embryo Proper Mature Embryo Suspensor Mature Arabidopsis Plant Differentiated Organ Globular Embryo The parts of a globular embryo undergo different fates
Late embryo development… Heart Stage TorpedoStage consists of cotyledon and axis development! 2 cotyledons
Mature Embryo Consists of: Cotyledons Axis - contains the shoot and root meristems
Part III: Why is Arabidopsis Thaliana a model plant? By Maria Garcia
Here’s Why • Arabidopsis Thaliana is convenient. It has a: • Fast generation time • Small genome • Large mutant collections • Large scientific community working on all aspects of plant biology
How fast does it grow? • Short non-seasonal generation time • Grows all year • 4 to 8 weeks from a seed to a mature plant
How small is it? • Arabidopsis has a small genome • 120Mb (25,000 genes- same as humans!) • Arabidopsis genome was sequenced in the year 2000
Easy to Manipulate • Large mutant collections • Chemical • Insertional • Knock-Out! • Easily manipulated • Genetically tractable
Everyone is in on it • Large scientific community working on all aspects of plant biology • Many resources on this plant already • Much is already known about this plant