Drell-Yan Di-Lepton Production: Understanding Asymmetries and Kinematic Scaling
70 likes | 202 Vues
This study explores Drell-Yan di-lepton production, focusing on the asymmetries that depend solely on parton distribution (PD) functions within the framework of semi-inclusive deep inelastic scattering (SIDIS). Each valence quark contributes to the diagram, and we discuss the kinematic variables (x_1, x_2) and the scaling in the full range of these variables. We examine experimental data with polarised beams and targets, emphasizing the importance of unpolarised beams in investigating (k_T) dependence of quark distribution functions. Our findings build on previous work, presenting new insights into angular distributions and asymmetries.

Drell-Yan Di-Lepton Production: Understanding Asymmetries and Kinematic Scaling
E N D
Presentation Transcript
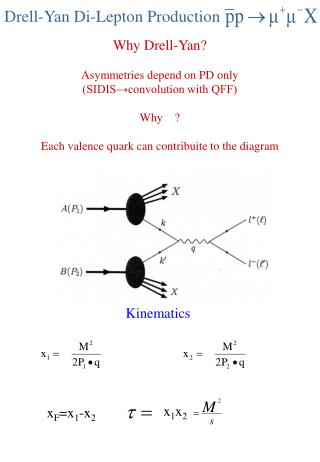
Drell-Yan Di-Lepton Production Why Drell-Yan? Asymmetries depend on PD only (SIDIS→convolution with QFF) Why ? Each valence quark can contribuite to the diagram Kinematics x1x2 xF=x1-x2
Drell-Yan Di-Lepton Production Scaling: Full x1,x2 range . needed [1] Anassontzis et al., Phys. Rew. D38 (1988) 1377
Drell-Yan Asymmetries Polarised beam and target To be corrected for: NH3 polarised target:
Drell-Yan Asymmetries Unpolarised beam and target Di-Lepton Rest Frame NLO pQCD: λ 1, 0, 0 Experimental data [1]: 30 % [1]J.S.Conway et al., Phys. Rev. D39(1989)92. involves transverse spin effects at leading twist [2]: cos2φ contribution to angular distribution provide: [2]D. Boer et al., Phys. Rev. D60(1999)014012.
Angular distribution in CM frame - + N + + - + X @ 252 GeV/c -0.6 < cos < 0.6 4 < M < 8.5 GeV/c2 • cut on PT selects asymmetry • 30% asymmetry observed Conway et al, Phys. Rew. D39 (1989) 92
Drell-Yan Asymmetries Unpolarised beam, polarised target Even unpolarised beam is a powerful tool to investigate кT dependence of QDF D. Boer et al., Phys. Rev. D60(1999)014012.
Weak decay B.R. = 0.9 % 36000 events / 100 days [1] Smith and Vogt Z. Phys. C75 (1997)271