Logical Framework Approach in Educational Planning
310 likes | 505 Vues
Learn about the Logical Framework Approach (LFA) for comprehensive project cycle management, including its history, key features, matrix, intervention logic, assumptions, verifiable indicators, and means of verification.

Logical Framework Approach in Educational Planning
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Topic:Logical FrameworkApproach Educational Planning
What isLFA? • LFA is a systematic planning procedure for complete project cyclemanagement • It is a problem solving approach which takes into account the views of allstakeholders • It also agrees on the criteria for project success and lists the majorassumptions
History ofLFA • Developed in response topoor planning and monitoring of Developmentprojects • The first logical frameworkdevelop of1960’s
KEY FEATURES OF LOGFRAMEMATRIX The LOGFRAME MATRIX isa participatory Planning, Monitoring & Evaluation tool whose power depends on the degree to which it incorporates the full range of views of intended beneficiaries and others who have a stake in theprogrammedesign. It is a tool for summarizing the key features of a programme and is best used to help programme designers andstakeholders
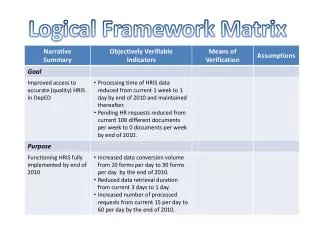
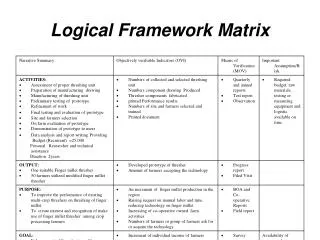
Summary of the logicalframework InterventionLogic • Goal – The higher level objective towards whichthe project is expected to contribute (mention targetgroups) • Purpose – The effect which is expected to be achieved as the result of theproject. • Outputs – The results that the project management should be able to guarantee (mention target groups) • Activities – The activities that have to be undertaken by the project in order to produceoutputs.
Cause-effect relationshipamong objectives at severallevels Goal Purpose Outputs Activities under full control of projectmanagement Inputs beyond controlof projectmanagement
Summary of the logicalframework Assumptions andPreconditions • Assumptions – Important events, conditions or decisions outside the control of the project which must prevail thegoal. – Important events, conditions or decisions outside control of the project management necessary for the achievement of the purpose. – Important events, conditions or decisions outside control of the project management necessary for the production ofoutputs. – Important events, conditions, decisions outside control of the project management necessary for the start of theproject.
Summary of the logicalframework Objectively Verifiable Indicators(OVI) • Goal – Measures (direct or indirect) to verify to what extent the goal isfulfilled. • Purpose – Measures (direct or indirect) to verify to what extent the purpose isfulfilled. • Outputs – Measures (direct or indirect) to verify to what extent the outputs are produced. • Activities(Inputs) – Goods, people and services necessary to undertake theactivities
Summary of the logicalframework Means of verification(MOV) • Goal – The sources of data necessary toverify status of goal levelindicators. • Purpose – The sources of data necessary toverify status of purpose levelindicators. • Outputs – The sources of data necessary toverify status of output levelindicators. • Activities – The sources of data necessary toverify status of activity levelindicators.
Objectively VerifiableIndicators • Indicators must be valid, reliable, precise, cost-effective and stated independently from otherlevels. • Indicators should make clear how the target group will benefit from the realisation ofoutputs. • Indicators should be specific in termsof: • Quality(what?) - Q • Quantity(how much?) - Q • Time (when,howlong?) - T • TargetGroup (who?) - T • Place (where?) - P
Key Features of Logframe Matrix(cont’d) • Develop a common understanding of the expectations of a programme by delineating a hierarchy ofaims; • Define indicators of success and establish criteria for monitoring and evaluation; • Define critical assumptions on which the programme is based;and • Identify means of verifying programmeaccomplishments
CORE CONCEPT OF LOGFRAME MATRIX: MEANS AND ENDLOGIC The main concept underlying the Logical Framework is means and end. The better the means and end linkages between each level of aims, the better the programmedesign. By definition, each programme has a “if-then” or “means-and-end” logic embeddedinit. If we produce certain results under certain conditions, then we can expect to achieve certain other outcomes.
LogFrame-Horizontallogic Aims measured by indicators through information collected and presented in specified means ofverification
THE LOGIC OF A PROGRAMME: A SET OF LINKEDHYPOTHESES then GOAL PURPOSE then if then OUTPUTS if ACTIVITIES if
PLANDOWNWARDS PLANDOWNWARDS Goal Assumptions Purpose Assumptions Outputs Assumptions Activities Assumptions Inputs ANDTHEN THINKUPWARDS
THE LOGICAL FRAMEWORK MATRIX Clear statementof: What we canaccomplish (outputs)and The important results we expect in the short to medium-term (purpose) and in the long term (goal)
Means ofverification The specific sources from which the status of each of the indicators can beascertained
Conclusion • A tool for planning a logical set of interventions • A tool for appraising a Programme document • A concise summary of theProgramme • A tool for monitoring progress made with regard to delivery of outputs and activities • A tool for evaluating impact of Programme outputs, This progress in achieving purpose andgoal.