Derailment Investigation
750 likes | 1.58k Vues
Derailment Investigation. By K.S.Chauhan Rtd . SSE (P.WAY)BB.CR. There are basically three type of derailments. Wheel derail in side the rail. Flange climbs the rail table.

Derailment Investigation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Derailment Investigation By K.S.Chauhan Rtd. SSE (P.WAY)BB.CR
There are basically three type of derailments • Wheel derail in side the rail. • Flange climbs the rail table. • Due to breakage of rail, wheel, axle, washing away the formation, or sabotage to track or wagon, coach. Obstruction on track etc.
Reasons Wheel derailed inside the track • Wheel shifted from axle. • Slack gauge of track. • Two stock at entering in switch.
Flange climbs the rail table • Off loading of wheels. • Excessive lateral oscillation of bogie. • Excessive side wears on rail and on wheel flange. • Hindrance in free movements of bogie. • Sharp edge on wheel flange to climb on T/Rail as well as on nose of crossing
Off loading of wheels- • Camber difference in bogie of wagon/ coach/`Loco Camber plays a very important role in keeping equal balancing load on each wheel, unbalancing the same will consequently lead to the off-loading of the wheel. • Uneven loading in wagon or shifting of load to one side of wagon.
For taking measurements- 1. In ICF coaches- • Clearance between axle box top and bogie frame bottom to be measured and difference in same axle or diagonally be calculated. • Clearance between bolster top and bogie frame bottom to be measured to assess balancing of load of coach on bogie. • Free heights of all springs to be measure to see the grouping of springs.(312mm to 321mm ) • A-321-318,B-318-315,C-315-312 • A load test of springs to be conducted to identify weak or stiff spring
2.Casnub wagon bogie – • Camber difference resulting in uneven load on LH or RH side of bogie • Free spring heights to check the correct grouping of springs.(251 mm to 260 mm) A-260-257, B-257-254, C-254-251 • Load test to check the weak and stiff springs. • Thickness of elastomeric pads
Excessive lateral oscillation of bogie. Causes- • Bent axle • Any breakage or jamming of Equalizing stay, Anchor link or Bump stops . • Wheel dia. difference • Excessive lateral Clearances
Hindrance in free movements of bogie. Causes-In ICF • Eccentric functioning of centre pivot. • Wearing of bronze piece, • Scratches on upper surface of bronze Piece, on bottom plate of side bearer, • Insufficient oil available in oil bath. • Insufficient oil available in pivot well. • Foreign material in oil of side bearer oil bath. -contd…
Wear in center pivot (in case of Casnub) • No lubrication in pivot housing (in case of Casnub) • Load on side bearer of Casnub bogie. • Over loading of wagons.
Bunching of load • Operational problems. 1-Application of SA/9 while entering the train in loop. 2-Fast acceleration and retardation while in full speed. Empty/light loaded wagon between loaded due to wrong marshalling
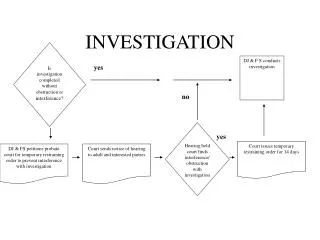
Important points to be observed at Derailment spot. • Reach at site before other supervisors and officers. Observe for investigation point of view- • Point of mount (POM), point of drop (POD) carefully • See whether POM is deep at gauge face of rail table, light mark or faint mark. Or wheel has directly came on rail table.
Corresponding drop mark of other side wheel inside the track. • The distance of Flange travelling on the rail table and drop mark outside the track. • Distance between POM and POD • The distance from POD to halt of derail wheel (dragging distance )
If more than one bogie or one coach/wagon is derailed check the ballast dust marks and dent marks on all the wheels so that first wheel derailed will be pointed out • Check for parts of derailed vehicle; old, broken or missing. • See whether any part of vehicle is lying before or after point of derailment.
Sign the loco defect card in a manner that no remark can be complied or can be made. Sketch of derailment site to be prepared. • Track measurements to be given to Sr.subordinates and associate with joint committee • Associate with restoration work.
Observe for restoration point of view- • (This can be done parallel to investigation activity by deputing co-supervisor) • Certify and convey the adjacent track is safe for traffic to engg.cor. • After assessing the damages; requirement of machines, material, labour force and supervisor to be conveyed to Engg.cor.
Make the shift to departmental and contractual labour and supervisor if time of restoration is likely to increase. • Give the advance memo to catering department for required meal and B/fast. • Ask IOW to provide tent and chairs. If work is going to take long time. • Arrangement of light if work is to continue at night.
Power observation- • Any adverse remark of driver in loco defect book. • Time taken for application of loco brake, from 5Kg to zero. • Check the loco movement on full application of brake up to 3 notches. • Check the current on each notch, find the gradualness. • Releasing time of brake. Zero to 5 Kg.
Other loco observation and measurements in stationary condition. • Brake cylinder strokes to be measured, to find out unequal braking on each wheel. • Wheel base to be measured. • Buffer heights to be measured. • Thickness of side bearer pads. • Spring heights under load. -contd….
Wheel gauge, wheel dia. • Wheel profile to check worn-out root radius for sharp or thin flange • Lubrication of centre pivot, any scratch marks, cut or dent marks. • Oil in side bearer, • Any foreign material in lubricant of side bearer and center pivot. • Scratches or dent, cut marks on side bearer base plate
THANK YOU ALL THE BEST