Scientific Method
260 likes | 505 Vues
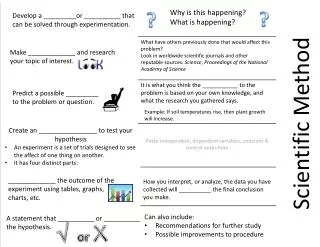
Scientific Method. Objective. Standards SPI 0807.Inq.1 Design a simple experimental procedure with an identified control and appropriate variables. I can… Identify the steps of the scientific method. Use the five senses to make an observation. Scientific Method (#80).

Scientific Method
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Objective Standards SPI 0807.Inq.1 Design a simple experimental procedure with an identified control and appropriate variables. I can… Identify the steps of the scientific method. Use the five senses to make an observation.
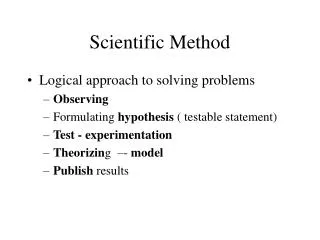
Scientific Method (#80) • Steps scientists use to answer questions and solve problems. I can identify the steps of the scientific method.
The Scientific Method Song http://singdancelearn.com/science-songs/scientific-method-song/
Observation (#64) • Any use of the senses to gather information • Smell, sight, feel, taste, sound I can use the five senses to make an observation.
Are the four liquids the same? What observations can you make about the four liquids? I can use the five senses to make an observation.
Objective Standards • 0807. Inq.1 Design and conduct an open-ended scientific investigation to answer a question that includes a control and appropriate variables. • 0807.Inq.2 Select tools and procedures needed to conduct a moderately complex experiment. I can… • Write a testable hypothesis for a scientific question. • Write a procedure for a simple experiment. • Identify basic laboratory tools (ruler, thermometer, graduated cylinder, beaker, balance, spring scale, stopwatch, microscope, magnifying glass, telescope, binocular, calculator, and computer). • Select the correct laboratory tool to make a measurement or observation.
Form a Hypothesis(#42) • Possible explanation • Answer to a question • Educated guess • Must be TESTABLE! • Will a plant grow better in sugar water? • Is there a difference in weight between a boiled egg and an uncooked egg? • How does salt affect the boiling point of water? I can write a testable hypothesis for a scientific question.
Write a hypothesis Will a plant grow better in sugar water? Is there a difference in weight between a boiled egg and an uncooked egg? How does salt affect the boiling point of water? I can write a testable hypothesis for a scientific question.
Test the Hypothesis • Write a procedure (step-by-step plan for an experiment) • Includes what to do for each step, materials needed, tools needed, amounts of substances used • Like a recipe for the experiment I can write a procedure for a simple experiment.
Laboratory Tools I can identify basic laboratory tools .
Write a procedure for making chocolate milk • Don’t forget any steps, no matter how simple they are. • Use exact amounts I can write a procedure for a simple experiment.
Objective Standards SPI 0807.Inq.1 Design a simple experimental procedure with an identified control and appropriate variables. I can… Define and identify the control group, experimental group, constant variables, independent variable, and dependent variablefor an experiment. Identify that the experimenter changes only one variable in a well designed experiment. (independent variable)
Test the hypothesis Control Group Experimental Group • Standard of comparison • Does not contain IV • Contains only constant variables (#20)(factors that are kept the same throughout the experiment) • Exposed to the IV I can define and identify the control group, experimental group, constant variables, independent variable, and dependent variable for an experiment.
Test the hypothesis Independent Variable (#43) Dependent variable (#22) • Factor that is deliberately changed • The experimenter (you) changes ONLY the IV. • Cause • Variable affected by changes in the independent variable • Usually the factor that is being tested or measured • Effect I can define and identify the control group, experimental group, constant variables, independent variable, and dependent variable for an experiment.
The Variables Song http://www.teachertube.com/viewVideo.php?video_id=77098&title=The_Variables_Song I can define and identify the control group, experimental group, constant variables, independent variable, and dependent variable for an experiment.
Examples Identify the IV, DV, and CV for each question below. Do robin eggs hatch more quickly at warmer temperatures? Does salt affect the boiling point of water? Do plants grow better in sugar water? I can define and identify the control group, experimental group, constant variables, independent variable, and dependent variable for an experiment.
Objective Standards • SPI 0807.Inq.3 Interpret and translate data in a table, graph, or diagram. • SPI 0807.Inq.4 Draw a conclusion that establishes a cause and effect relationship supported by evidence. • SPI 0807.Inq.5 Identify a faulty interpretation of data that is due to bias or experimental error. I can… • Choose the correct type of graph (line, bar, or circle) to use with a data table. • Choose the best conclusion based on the results of an experiment. • Write a valid conclusion for an experiment. • Identify examples of bias and experimental error.
Analyze Results Data Table: contains sets of data in a chart form Bar Graph: compare things between different groups Line Graph: track changes over time Circle Graph: show parts of a whole or percentages
Conclusion • Includes a summary of the findings of the experiment, states whether the hypothesis was supported, and addresses any problems that happened. • Does the data support the hypothesis? • Does more testing need to be done? • Were there any experimental errors? • It is OK if the conclusion does not support the hypothesis!!!!! • Conclusions often lead to new scientific questions and experiments! I can choose the best conclusion based on the results of an experiment.
Experimental Error • Bias: intentionally or unintentionally favoring one thing over another • Experimental error • Measuring incorrectly • More than one independent variable • Miscalculations • Mixing the wrong things together I can identify examples of bias and experimental error.