Female Reproductive Organs
180 likes | 436 Vues
Sex Education:. Female Reproductive Organs. Female External Genitals. 4. 1. 3. 5. 6. 2. Female Internal Reproductive Organs . 14. 15. 9. 10. 11. Endometrium. 8. Bladder. 13. Urethra. 12. Female Internal Reproductive Organs (Continued).

Female Reproductive Organs
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sex Education: Female Reproductive Organs
Female External Genitals 4 1 3 5 6 2
Female Internal Reproductive Organs 14 15 9 10 11 Endometrium 8 Bladder 13 Urethra 12
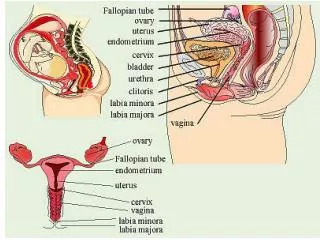
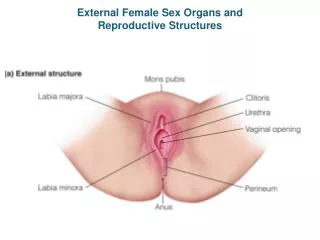
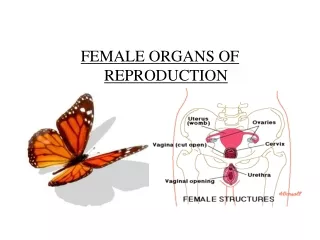
Female Reproductive Organs Vulva: • external female reproductive organs Labia majora (outer): • fatty outer border on either side of the vaginal and urethral opening • line of protection Labia minora (inner): • two smaller folds of skin on either side of the vaginal and urethral opening • line of protection Vaginal Opening: • is an opening that lies between the labia minora
Female Reproductive Organs Hymen: • a thin membrane • may tear during physical activity Urethra Opening: • opening where urine is secreted Clitoris: • contains many nerve endings and blood vessels • highly sensitive • plays a major role in sexual arousal Vagina: • elastic, muscle lined tube also called birth canal • stretches to allow for birth of baby
Female Reproductive Organs Cervix: • opening to the uterus • dilates to 10 cm during childbirth • gland that secretes mucus to lubricate vagina Uterus: • upside down pear shaped hollow muscular organ • primary function is to hold and nourish the developing embryo and fetus Endometrium: • a thin lining of the uterus • provides attachment to the embryo
Female Reproductive Organs Fallopian Tubes: • tubes on each side of the uterus that connect the uterus to the ovaries • very narrow, lined with hair-like projections(cilia) • motions of cilia release ovum(egg) into the fallopian tubes Ovaries: • two female sex glands • produce mature ovum(egg) • produce female hormones: progesterone and estrogen
SEX EDUCATION Female Reproductive Disorders
Female Reproductive Disorders Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): • An infection of the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and the surrounding areas of the Pelvis • It can damage the female reproductive organs • It is caused by Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD’s) Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS): • Caused by bacteria that produces a toxin that affects the immune system and liver • Symptoms: fever, chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and rashes on the hands and feet • Caused by tampons being left inside the vaginal canal too long • If caught early: treated by antibiotics • Tampons should be kept in no longer than 2 to 4 hours
Female Reproductive Disorders Vaginitis: • Inflammation of the vaginal tissue • Symptoms: discharge, burning, and itching • Treated by: antibiotics Yeast Infections: • Caused by fungus • Characterized by a thick, white, odorless discharge • Symptoms: itching, burning, and painful urination • Treated by: over the counter medication Ovarian Cyst: • Fluid filled sac on ovary • No signs or symptoms • Treatment: surgically removed or can disappear on their own
Female Reproductive Disorders Breast Cancer: • The most common form of cancer in women • Symptoms: change in breast or nipple appearance, a lump or swelling in the breast, a lump in the arm pit, and/or discharge from the nipple • Treatment: radiation, chemotherapy, or removal of breast • Breast Self Exam: should be performed every month • Mammogram: a series of X-Rays of the breast that should be done after the age of 40 Ovarian Cancer: • Cancer of the ovaries • Symptoms: abdominal pressure, nausea, indigestion, urinary frequency, constipation, diarrhea, abnormal bleeding, weight gain or weight loss, and fatigue • Treatment: radiation, chemotherapy • Early detection is critical because only 25% of women survive beyond 5 years if the cancer is diagnosed in advanced stages
Female Reproductive Disorders Cancer of the Cervix • Detected by Pap Test: • a test that uses a cotton swab to collect cells from the cervix, and it detects abnormal cells • Females should have Pap Test done yearly from the age of 18 unless sexually active • NO Symptoms • Treatment: radiation, chemotherapy • Uterine Cancer: Cancer of the Uterus • Symptom: abnormal bleeding • Treatment: radiation, chemotherapy, & hysterectomy