The Nervous System
230 likes | 314 Vues
Learn about the control, coordination, and communication roles of the nervous system, including the central and peripheral components, brain parts, neuron functions, and feedback mechanisms.

The Nervous System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Functions of the Nervous System • Control and coordinate functions throughout the body • Respond to internal and external stimuli
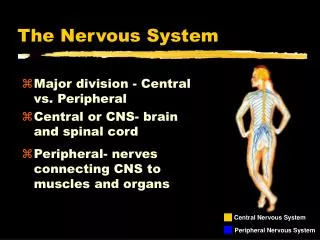
Parts of the Nervous System • The Central Nervous System • Consists of the brain and spinal cord • The Peripheral Nervous System • Consists of the nerves that are not part of the brain or spinal cord (ex. Nerves in the arms and legs)
Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (Brain and Spinal cord) Peripheral Nervous System (nerves that are not part of the brain or spinal cord)
Central Nervous System Parts of the Brain • Cerebrum • Responsible for voluntary activities of the body • Ex.-moving the muscles
Parts of the Brain • Cerebellum • Responsible for coordination and balance of the actions of the muscles • Helps the body to move gracefully and efficiently
Parts of the Brain • Brain Stem • Regulates information flow between the brain and the rest of the body • Thalamus • Receives messages from the body and relays them to the cerebrum (voluntary actions) • Hypothalamus • Recognizes and regulates hunger, thirst, fatigue, and body temperature
Parts of the Brain Cerebrum Hypothalamus Thalamus Cerebellum Brain Stem
The Spinal Cord • The major communication link between the brain and the rest of the body • A reflex is a quick automatic response to a stimulus
Neurons-cells of brain tissue • Impulses are electrical signals carried by the nervous system • The cells that carry these impulses are called neurons
Parts of a Neuron • Cell body • Contains the nucleus and cytoplasm • Dendrites • Carry impulses toward the cell body • Axon • Carries impulses away from the cell body
The Resting Neuron • Not transmitting an impulse • If the outside of the cell has a positive charge and inside of the cell is a negative charge, then the neuron is said to be at resting potential
Where do these charges inside the cell and outside come from? • Sodium Potassium Pump-make changes in notes • Cell membrane pumps Na+ ions INTOof the cell and K+ OUTthe cell by active transport. • A difference in charges has to occur for the neuron to become active and transmit messages.
The Moving Impulse • A neuron remains in its resting state until it receives an impulse • An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or the environment
The Moving Impulse • Na+ ions flow into the neuron and the inside of the cell temporarily becomes more positive than the outside • The change from negative to positive is called a nerve impulse or an action potential • The impulse travels down the axon away from the cell body
The Moving Impulse • As impulse passes K+ flows out of the neuron and the resting impulse is restored. The neuron has a negative charge on the inside and a positive charge on the outside.
The Synapse • The location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell
Neurotransmitters • Chemicals used to transmit an impulse across a synapse to another cell
Questions from Thermoregulation image Stimulus: low body temperature Response: _________________ Type of Feedback: ___________ Stimulus: high body temperature Response: __________________ Type of Feedback: ____________
Questions from child birth image Stimulus: baby’s head pushing on the cervix Response:___________________________ Type of Feedback: ____________________