Understanding the Functions and Injuries of the Spinal Cord
120 likes | 236 Vues
The spinal cord is a vital extension of the central nervous system, housed within the vertebral column. It protects nerve roots and internal organs while providing a base for muscle and tendon attachment, whether standing, sitting, or laying down. Its structural support facilitates balance and mobility through flexion, extension, bending, and rotation. Spinal cord injuries (SCI) can lead to significant mobility or sensory loss, with varying effects based on injury location. Notable conditions include Scheuermann's Kyphosis, Scoliosis, and Lumbar Lordosis. Protect your spinal health!

Understanding the Functions and Injuries of the Spinal Cord
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Spinal Functions By Chrissy And Erika
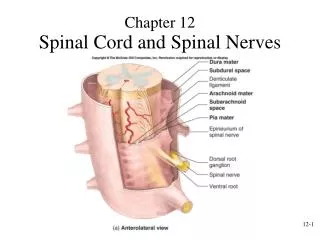
What is the Spinal Cord? • A long and thin tubular bundle of nerves that is an • extension of the central nervous system from the brain and is enclosed and protected by the bony vertebral column.
Protection • Protects the spinal cord and nerve roots which lie • under the boney structure • Protect many internal organs • Base for Attachment • Attaches the pelvic and pectoral girdle • Attaches various tendons and ligaments • Attaches muscles • http://www.becomehealthynow.com/article/bodyspine/800/
Structural Support • Supports all parts of the skeleton while sitting, standing, laying, etc. • Connects the upper and lower body • Helps balance weight distribution • Flexibility and Mobility • Flexion • Extension • Side bending • Rotation • http://www.becomehealthynow.com/article/bodyspine/800/
Spinal Cord Injuries • A Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that results in a loss of mobility or feeling • Very different from other back injuries such as a ruptured disk or a broken back • The extent of the injury depends on where the injury is on the spinal cord
The Injuries • Cervical injuries usually end in quadriplegia • Injuries above C4 may require the person to have a • ventilator for breathing • C5 injuries result in no hand or wrist control, but some • bicep and shoulder control • C6 injuries result in wrist control, but no hand control • C7 and T1 injuries result in arm straightening, but still • some dexterity issues • T1-T8 there is usually poor trunk control because of • loss of abdominal muscle movement • Lumbar and Sacral injuries result in loss of control of • hip flexors and legs • http://www.spinalinjury.net/html/_spinal_cord_101.html
Scheuermann’s Kyphosis of Thoracic spine Scoliosis
Lumbar Lordosis Lumbosacral Transitional Vertabrae