Hormonal Signal Transduction and Nutrient Processing in Cells
60 likes | 194 Vues
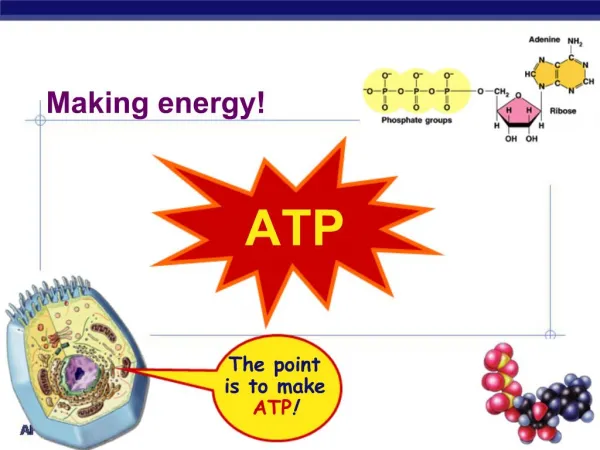
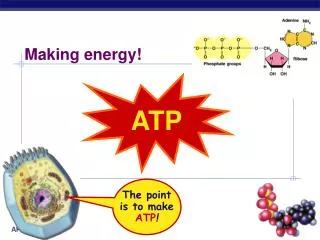
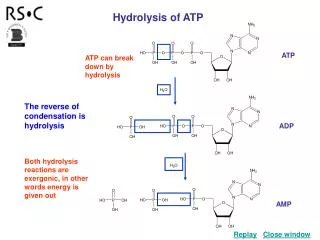
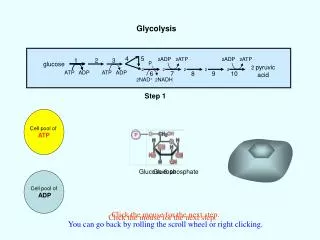
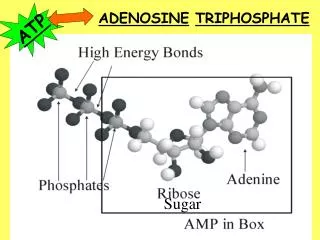
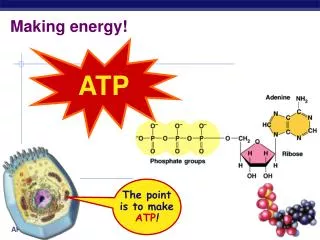
This process outlines how receptor proteins receive hormones, initiating a cascade that leads to protein synthesis and nutrient processing within the cell. The hormone binds to the receptor, triggering a series of steps where DNA is transcribed to RNA, which is then translated into proteins by ribosomes. These proteins are transported to the Golgi apparatus for maturation before being released. Additionally, it describes how food enters the cell through endocytosis, and how enzymes from lysosomes break down the food into sugars, which mitochondria use to produce ATP.

Hormonal Signal Transduction and Nutrient Processing in Cells
E N D
Presentation Transcript
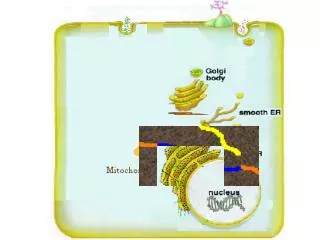
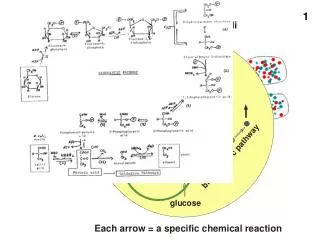
1. Receptor Protein recieves Hormone 2. Hormone goes in 3. Transport vesicle floats 4. Hormone calls for info to be copied. 5. DNA copied to RNA 6. RNA leaves into the ER. 7. Ribosome reads RNA and builds Protein 8. Vesicle leaves ER for proteins to mature in Golgi 9. Vessicle floats 10. Vesicle fuses with Golgi Body 11. Vesicle leaves Golgi 12. Hormone released.
A. Food enters via endocytosis B. Lysosome from Golgi bumps (made in step 10) into vesicle C. Two vesicles fuse D. Enzymes dissolve food into sugar E. Sugars uptaken by mitochondria to make ATP. 1. Receptor Protein recieves Hormone 2. Hormone goes in 3. Transport vesicle floats 4. Hormone calls for info to be copied. 5. DNA copied to RNA 6. RNA leaves into the ER. 7. Ribosome reads RNA and builds Protein 8. Vesicle leaves ER for proteins to mature in Golgi 9. Vessicle floats 10. Vesicle fuses with Golgi Body 11. Vesicle leaves Golgi 12. Hormone released.