Optimizing Fiber Positioning and Integration Timing in Telescopic Instrumentation
120 likes | 241 Vues
This toy model promotes discussions on PFI setup time trades, based on arbitrary parameters and assumptions. It includes a timing diagram showing various steps in the process, such as Cobra move, MC integration, calibration, and centroiding. The model calculates Cobra move time, MC integration time, and the number of finished fibers based on positioning errors and move distances. Inputs include positioning errors and minimum move time, while internal parameters involve Cobra velocity and angular velocities. The model aims to optimize integration time based on positioning and seeing limits to maximize observing efficiency. It also analyzes the impact of integration time on science fiber positioning success.

Optimizing Fiber Positioning and Integration Timing in Telescopic Instrumentation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PFS setup timing model Peter Mao
WARNING • This is a toy model. It is intended to promote discussion of PFI setup time trades. • Assume that all parameters and assumptions made here were pulled from thin air.
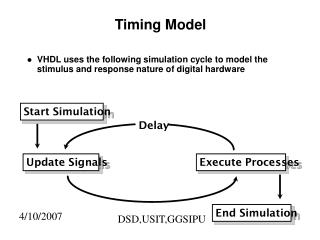
Timing diagram (schematic) close shutter, read out CCD telescope slew/settle cobra anti-home, cobra scan to home w/ MC integration MC readout, calibration, centroiding calculate distortion map iteration sequence transfer new targets Cobra move MC integrate MC readout, calibration, centroiding ID centroids, calc SF PFI(x,y) ASIAA repeat done JPL Caltech report final status to OBCP/SOSS Other
Positioning error model • Presently, derived from C.Fisher’s 2008 data on Cobra convergence. • The calibrated (red) curve has a functional dependence: • d = d010-0.6(n) • with d = distance in microns, interpreted as the 1 stdev distance in a 2D gaussian distribution. • and n = iteration • This is used to calculate • 1. the Cobra move time • 2. the MC integration time • 3. the number of (un)finished fibers
Cobra move time • move time should be a function of the distance error. probably a linear function. • INPUTS: • positioning error (d) [microns] • miminum move time (default: 0.01 sec) • INTERNAL PARAMETERS: • Cobra velocity (5000 microns/sec) • This should really be sorted out in (θ,ϕ) space, not in cartesian coords. • For initial moves, the angular velocity is 2π rad/sec. • When angular errors are smaller (< 10 deg) cobra moves at π/2 rad/sec. • High velocity is likely only used for the first two iterations. • Assume Cobras are moved in 5 groups. • FUNCTION • t = (tmin < d/v) * 5
MC integration time • integration time should scale inversely with required accuracy • required accuracy should be proportional to distance error (of the next step) • INPUTS: • MC allowed position error [function of cobra position error] • using d/10 for now. • seeing limit [in microns now, but should be in arcsec] • integration time at seeing limit [default = 10 sec] • minimum exposure time (default = 0.1 sec) • FUNCTION • C = dseeing * tseeing • dMC = (dseeing < dcobra/10) • tMC = (tmin < C/dMC)
# finished fibers • Assume that SF locations are Gaussian-distributed about the desired position, and that the position error, d, is the standard-deviation of that distribution. • INPUTS • position error [d = d(iteration step)] • number of science fibers • error budget allocation for SF location (dmax) • Nfibers_on = floor(NSF * (1 – exp(-0.5 * (dmax/d(n))2) • NSF = Nfibers_on + Nfibers_off
Sample output • Study of fiber efficiency vs. MC integration time at seeing limit. • Based on timing model: • giving up 27 fibers breaks even if the MC integration time at the seeing limit drops by ~5 seconds. • up to 5 seconds, the MC integration time is a subdominant factor in observing efficiency. • Trade can be calculated for any variable in the timing model dBη = 10 log10(η) η = (# observed)/(max observable) 1 Fiducial fiber = 0.8 Science fibers
Loose ends • Cobra timing models needs to be updated • MC timing model needs input from ASIAA • Setup excecution sequence will evolve during development • All parameters need to be vetted.