Introduction to the Laplace Transform: Definitions, Properties, and Applications in DEs
590 likes | 930 Vues
This chapter covers the fundamentals of the Laplace Transform, including its definition, basic properties, and methods for solving differential equations (DEs) using both the Laplace and inverse Laplace transforms. You'll learn how to compute the Laplace Transform for various functions, apply theorems related to derivatives, and utilize operational properties effectively. The content is structured to facilitate understanding and application in solving initial value problems through practical examples and exercises.

Introduction to the Laplace Transform: Definitions, Properties, and Applications in DEs
E N D
Presentation Transcript
THE LAPLACE TRANSFORM Chapter 4
Plan I - Definition and basic properties II - Inverse Laplace transform and solutions of DE III - Operational Properties
I – Definitions and basic properties Learning objective At the end of the lesson you should be able to : • Define Laplace Transform. • Find the Laplace Transform of different type of functions using the definition.
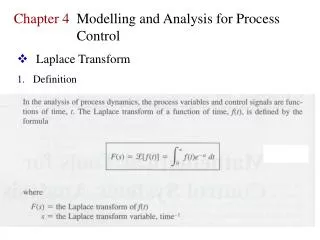
Definition: Laplace Transform Let f be a function defined for Then the integral is said to be the Laplace transform of f, provided that the integral converges.
Use the definition to find the values of the following: Example 1
Example2 Find the Laplace transform of the function
Transform of a Piecewise function Example 3 Given Find
Laplace Transform of a Derivative Let Find
Laplace Transform of a Derivative Theorem where
Laplace Transform of a Derivative Example Find the Laplace transform of the following IVP
Laplace Transform of a Derivative Solution
Laplace Transform of a Derivative Solution
II – Inverse Laplace Transform and solutions of DEs Learning objective At the end of the lesson you should be able to : • Define Inverse Laplace Transform. • Solve ODEs using the Laplace Transform.
Inverse Transforms If F (s) represents the Laplace transform of a function f (t), i.e., L {f (t)}=F (s) then f (t) is the inverse Laplace transform of F (s) and,
is a Linear Transform Where F and G are the transforms of some functions f and g .
Example 1 Solve the partial given IVP by Laplace transform.
III – Operational Properties Learning objective At the end of the lesson you should be able to use translation theorems.
First translation theorem If and is any real number, then .
First translation theorem Example 1: .
First translation theorem Example 2: .
Inverse form of First translation theorem Example 1: .
Exercise Solve
Unit Step Function or Heaviside Function The unit step function is defined as U 1 t
Example What happen when is multiplied by the Heaviside function
Example f f t 0 0 2 t -3 -3
The Second Translation Theorem If and then
Example 1 Let then
Example 2 Find where