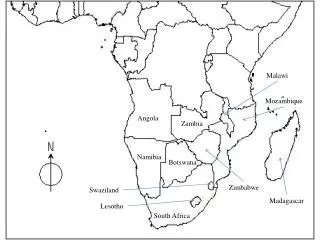
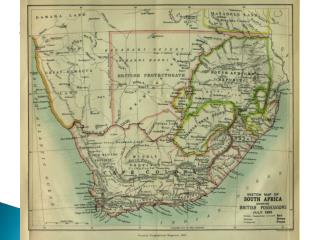
South Africa
240 likes | 435 Vues
South Africa. By: Paul M., TJ M., Matt C., and Sumi C. Map Before. Map After Zulu War. Modern Map. Initial Occupation. Provisions S tation at Cape Town T ip of Africa Dutch, French, and Germans; Boers C oastal areas Britain seize control Pushed Boers to the interior

South Africa
E N D
Presentation Transcript
South Africa By: Paul M., TJ M., Matt C., and Sumi C.
Initial Occupation • Provisions Station at Cape Town • Tip of Africa • Dutch, French, and Germans; Boers • Coastal areas • Britain seize control • Pushed Boers to the interior • Diamond and gold discovered • Britain annexed parts of South Africa
Benefits to the Imperial Power • Supply Station • Diamond • Gold • Power in Africa
Treatment of Indigenous People • Apartheid • Separate Bathrooms • All Minorities Beaten and Harrassed
Indigenous Perspective • Gold was found • South African Republic president; Paul Kruger • Kruger tries to lessen long-term dependence on Cape merchants • Developed rail-link to Portuguese East Africa to block British from Gold
Resistance & Independence Movements • Union of South Africa • African National Congress • Nelson Mandela
Benefits to Indigenous People • Diamonds in 1867 • Gold in 1886 • Protection of Imperial Rule
Culture Imperialism • Discrimination • Leads to Apartheid • British destroyed the Pedi • Obtained laborers for the Kimberly mines
The Dutch Arrival • In 1652, the Dutch arrived in South Africa at the Cape of Good Hope. This was to develop forts and vegetable gardens for the ships of the Eastern Trade.
The British Take Over • The British take over Cape Colony in 1795 • The Dutch regained control of Cape Colony in 1802 • Britain takes it over again a few short years later (1806) • The location was important Britain because of the strategic route to India.
The Discovery of Diamonds and Gold • The discovery of diamonds and gold started the British rule of south Africa. • The British begin to expand north of Kimberly where gold was discovered. • Consequently this began wars of resistance against the imperialism of South Africa.
The Zulu War • Began in 1879 and ended 2 years later • The Battle of Rorke’s Drift was the major battle in this war • 139 Britsh troops defeat about 4500 Zulus in this battle • The Zulu’s had to be removed for the British to try and unite black and white under their rule
The Boer War • The Boers • The Boers were Dutch speaking settlers of South Africa • This war was actually two different wars fought between the two Boer republics and the British Empire • These republics were known as the Orange Free State and the South African Republic
The Boer War • The War • The war began in 1899 and ended 1902 • Britain took over the two Boer republics after they were defeated • A treaty was signed to end the war • Eight years later the Union of South Africa was created
The African National Congress • Fomed in 1912 • It was formed to unite the African people • The ANC helps the struggle for political, social and economic changes • The ANC still exists today • The ANC constitution was renewed in 1996 • It was banned during the apartheid era
Apartheid • Apartheid is a policy of racial segregation against non-whites • In 1948 the apartheid laws were inforced • The ANC leader Nelson Mandela led a campaign of civil disobedience in 1950. • In 1964 Mandela is sentenced to life in prison • The ANC is unbanned and Mandela is released, the start of the end of apartheid
The Sharpeville Massacre • Occurred in 1960 at the police station in Sharpeville • Black protesters were shot down after outnumbering police • 69 people were killed • Protest was organized by the ANC
The End of Apartheid • The ANC win election • The first non-racial election • Mendela is elected as the president • South Africa takes a seat in the UN after 20 years
Modern Status • South Africa is doing better today is isn’t considered to be a 3rd world country at this point in time. HDI: 0.597 GDP: 5.3% Literacy Rate: 88% • Imperialism caused the South African’s to unite and are still united today • There are 9 provinces in south africa
References • http://countrystudies.us/south-africa/66.htm • http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/1069402.stm • http://africanhistory.about.com/od/slaveryinsouthafrica/p/SlaveTimeline.htm • http://www.britishbattles.com/zulu-war/rorkes-drift.htm • http://www.historyofwar.org/articles/wars_zulu.html • http://school.eb.com/all/eb/article-9007978?query=apartheid&ct=null • http://www.mapsofworld.com/south-africa/history/imperialism.html