Proving Equilateral and Congruent Triangles: A Comprehensive Guide
90 likes | 191 Vues
This resource covers the essential principles and theorems related to the congruence and properties of triangles. It begins with the properties of equilateral triangles, specifically illustrating how to prove triangle DEF is equilateral given triangle ABC is equilateral. The document further discusses the AAS Theorem and the HL Theorem, providing methods for proving triangle congruency. Additionally, there are exercises involving triangle angles and geometric shapes such as regular pentagons and squares to reinforce learning through practical applications.

Proving Equilateral and Congruent Triangles: A Comprehensive Guide
E N D
Presentation Transcript
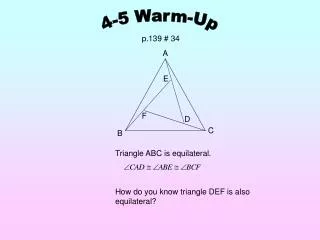
4-5 Warm-Up p.139 # 34 A E F D C B Triangle ABC is equilateral. How do you know triangle DEF is also equilateral?
Warm-Up C F Given: E B D A Prove:
Other methods of Proving Triangles Congruent Theorem 4-3: AAS Theorem If two angles and a non-included side of one triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent.
Hypotenuse: The side opposite the right angle in a right triangle. hypotenuse leg leg Theorem 4-4: HL Theorem If the hypotenuse and a leg of one right triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent.
X Given: 1 2 Prove: 3 4 B A Y
P Given: 3 5 6 4 Prove: Q T 1 2 R S
HW: p. 143-145 #1-19 odd skip # 9
U O T 2 1 A D B C Given: Prove:
A B E F C D G ABCDE is a regular pentagon and DEFG is a square. Find: angles EAF, AFD, DAF