Mutations
380 likes | 1.17k Vues
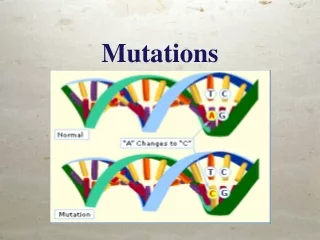
Mutations. What is a mutation?. A mutation is a change in genetic material Two kinds of mutations: Gene mutations Chromosomal mutations. Gene Mutations. Produce changes in a single gene Point mutation – changes in one or a few nucleotides Deletion Addition Substitution.

Mutations
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is a mutation? • A mutation is a change in genetic material • Two kinds of mutations: • Gene mutations • Chromosomal mutations
Gene Mutations • Produce changes in a single gene • Point mutation – changes in one or a few nucleotides • Deletion • Addition • Substitution
Mutations Practice • ATACGTCAAGAC • ATACGCAAGAC • ATACGTCAAGAC • ATACGTACAAGAC • ATACGTCAAGAC • ATACGCCAAGAC Deletion Insertion Substitution
Changes caused by mutations • ATAACCCAAATC • UAU UGG GUU CUG • Tryosine- Tryptophan – Valine • ATUACGCAAATC • UAU UGC GUU CUG • Tyrosine – Cysteine -Valine
Frameshift Mutation • Shifts the reading frame of the genetic message • ATAACCCAAATC • ATAACCAAATG
Chromosomal Mutations • Changes in the structure of a chromosome
Gene Regulation • Only some genes need to be expressed at any given time. • Some genes are transcribed while others remain silent. • How are genes turned “on” or “off”?
Operon • Operon • Cluster of genes • Found in prokaryotes
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation • TATA box • Short region of DNA • Found before the gene • Helps position RNA polymerase before transcription