Babylon
220 likes | 1.27k Vues
Babylon. By Robert, Jake, Julius, and Adrian. Babylonia’s Significant Historic Figures. King Hammurabi Created the first large uniform collection of laws (an eye for an aye, a tooth for a tooth). King Hammurabi pushed Babylon’s boundaries north to Mari and south to Ur during his reign

Babylon
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Babylon By Robert, Jake, Julius, and Adrian
Babylonia’s Significant Historic Figures King Hammurabi • Created the first large uniform collection of laws (an eye for an aye, a tooth for a tooth). • King Hammurabi pushed Babylon’s boundaries north to Mari and south to Ur during his reign King Nebuchadnezzar • Built the Hanging gardens of Babylon • Captured Jerusalem and caused the Babylonian exile
The Government and Laws of Babylon Laws • Used the uniform code of Hammurabi which touched on every crime imaginable • The code had equal punishment for each crime (an eye for en eye, a tooth for tooth) however, the code’s punishment changed based upon the class of the criminal and the affected by the crime committed • The code had 282 laws in total • The code of Hammurabi was written on a large black pillar with a picture at the top of Shamash the sun god handing king Hammurabi the law code Government • Government was lead by strong kings • It was a strong central government that was fair to all citizens and easily controlled • The economy was completely controlled by the government, thus there were no private businesses • Priests were placed in charge by Hammurabi to help control the economy
Existing Jobs in Babylonia • Architect • engineer • exorcist • charioteer • cavalryman • Musician • servant • Priest • bitumen-carter • rope-maker • farmer • scribe • tax collector • overseer • herder • weaver • merchant. • Brick maker • bricklayer • brick-stamper • basket-maker • potter • smith goldsmith/silversmith • Jeweler • Baker • Gardener • wine-maker • Cook • Wheelwright • furniture-maker • boatman • Boat builder • carpenter • horse-trainer
Human Expression Writing and Language • Wrote on cuneiform on clay tablets which was associated with the Acadian language • They were Semitic speaking • Used Cuneiform for writing but, it was not well known, so they began to use the Aramaic language for writing. With this was introduced the first alphabetical script. Aramaic was a Lingua Franca. • Wrote on clay tablets Art
The Architecture of Babylon Architecture • used mud-brick construction • had walls articulated by pilasters and recesses, sometimes faced with burnt and glazed brick • had narrow rooms, mostly covered with flat timber and mud roofs • used extensive use of bitumen in drain and pavement construction and as mortar. • Dyed clay bricks. City Planning • The palace was located near one of the main entrance/gate (Ishtar Gate) to the city and it was next to the processional way. • The processional way was very wide and it was paved with large stone slabs on bitumen. It was also a walled road. • The houses were not freestanding, and were built together. • It had eight gates
Religion • Beliefs • The Babylonians believed that the king/monarch was a god, or that he had a divine origin • They believed that the gods revealed the future in the entrails of sacrificed animals The Gods of Babylon • Marduk - the city god • Shamash - the sun god • Nabu - the god of writing • Ishara - the goddess of love • Gula - the goddess of healing • Ea – the god of water and wisdom • Ishtar – the fertility goddess • Sin – the moon god • The Babylonians didn’t believe in an afterlife that held any promise or threat
The Babylon’s Accomplishments • The Babylonians created the hanging gardens of Babylon under King Nebuchadnezzar • The Babylonians created the first large collection of laws under King Hammurabi • Developed sundried clay bricks which they dyed different colors, and the clay could be found in different colors • Under King Hammurabi, a very effective workforce was created due to his code.
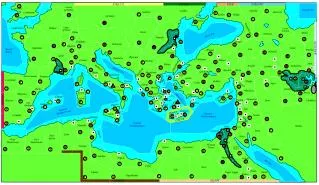
Map of the Babylonian Empire at the Heights of its Power Babylonia under Hammurabi The Neo Babylonian Empire • Map of the Babylonian empire under the reign of king Hammurabi (from about 1792 BC – 1750 BC)
The Questions 1.Why was this civilizations significant in ancient Mesopotamia? • The Babylonians reunited Mesopotamia, and if they hadn’t done this, many empires wouldn’t have been founded • The Babylonians rebelled and burned Nineveh (the capital city of the Assyrians) to the ground, ending the Assyrian empire 2.Why is this civilization important in the modern world? • This civilization is important to the modern world because of what it was. Babylon showed that great numbers of people could work together. If they hadn’t done that many of the very populated cities wouldn’t be here because people wouldn’t know how to keep hundreds of thousands of people under control. 3.Should this civilization be included in the curriculum about ancient Mesopotamia? Why? • Yes. It should. At its height, Babylon was one of the largest, most important cities of the ancient world. It was located in central Mesopotamia, near the point where the Tigris and Euphrates flow closest to one another. This same region has been home to many capital cities over the centuries: Kish, Agade, Seleucia, and Baghdad among them.