1.2 The Modeling Process
60 likes | 191 Vues
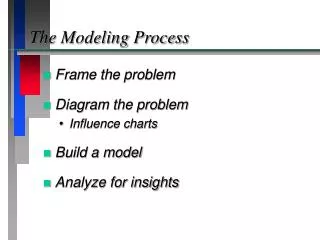
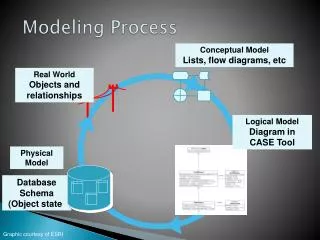
The modeling process involves applying methods to analyze complex, real-world problems, enabling predictions about outcomes based on various actions. Key concepts include stochastic behavior, where randomness affects outcomes, and the distinction between static and dynamic models—static does not account for time, whereas dynamic does. Additionally, continuous vs. discrete modeling highlights how time is treated. Verification ensures the model functions correctly, while validation confirms it meets the problem's requirements, essential for effective problem-solving.

1.2 The Modeling Process
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is Modeling? Modeling is the application of methods to analyze complex, real-world problems in order to make predictions about what might happen with various actions.
*Στόχος = “aim” or “guess” Stochastic* Behavior A system exhibits probabilistic or stochastic behavior if an element of chance exists. A probabilistic or stochastic model exhibits random effects, whereas a deterministic model does not.
Πάντα ῥεῖ Static vs. Dynamic Models A static model does not consider time, whereas a dynamic model changes with time. Heraclitus (ca. 535–475 BC)
Continuous vs. Discrete In a continuous model, time changes continuously, while in a discrete model, time changes in incremental steps. Zeno of Elea (ca. 490 BC? – ca. 430 BC?)
Verification vs. Validation The process of verification determines if the solution works correctly, while the process of validation establishes if the system satisfies the problem’s requirements.