HPLC
E N D
Presentation Transcript
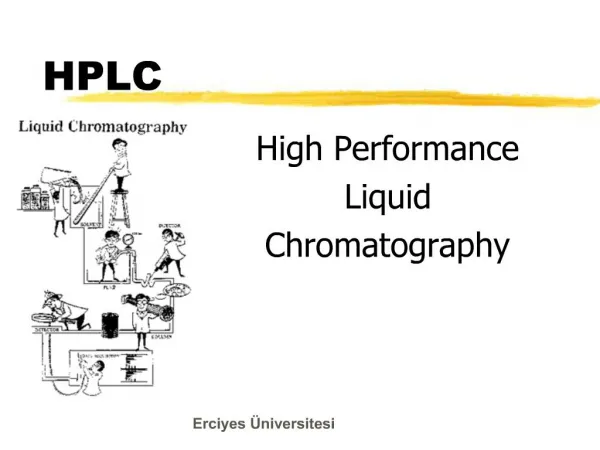
1. HPLC High Performance/Pressure
Liquid Chromatography
2. Advanced Instrumentation
3. The System
4. Columns
6. Reversed Phase Chromatography Packing is nonpolar
Solvent is polar with respect to the sample.
Retention is the result of the interaction of the nonpolar components of the solutes and the nonpolar stationary phase - hydrophobic.
7. Reversed Phase Chromatography - 2 Bonded phases made by covalently bonding a molecule onto a solid stationary phase like silica
Typical stationary phases are nonpolar hydrocarbons, waxy liquids or bonded hydrocarbons (such as C18, C8, C4, etc.)
pH range 2.5 to 7.5 ONLY (or the column degrades)
60-90% of all analytical LC separations are done on bonded phases in the reverse phase mode.
8. Reversed Phase Chromatography - 3 Solvents are polar aqueous-organic mixtures such as methanol-water or acetonitrile-water.
Elution can be either:
�Isocratic� � use only one buffer
�Gradient� � mix in a second buffer
9. Capacity Analytical: ng down to fg
Semi-prep: mg to ug
Preparative: g
Industrial: kg
10. Solvents Clean
HPLC grade
Filtered
Degassed
Water
Polar
Methanol or
Acetonitrile
Maintain pH
TFA
11. Tubing Very small inner diameter
Consistent i.d.
Very strong
Easy to cut
Fittings available
12. Injector
13. Pumps
14. Pump schematic
15. Pump cycle
16. Detector
17. Detector schematic
18. Fraction collector
19. Recorder
20. Direct to computer
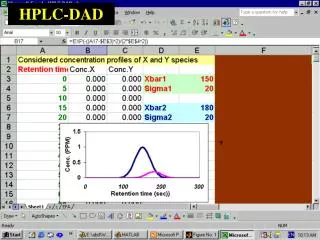
21. HPLC Data
22. HPLC Data
23. HPLC Data Analysis