ATM
140 likes | 471 Vues
ATM. Yang Wang 103301 Professor: Anvari. Definition. 1: ATM is a high bandwidth, low-delay, connection-oriented, packet-like switching and multiplexing technique. 2: It is a very high speed transmission technology. Switching and Transmission Technologies. 1: Switching Technology

ATM
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ATM • Yang Wang • 103301 • Professor: Anvari
Definition • 1: ATM is a high bandwidth, low-delay, connection-oriented, packet-like switching and multiplexing technique. • 2: It is a very high speed transmission technology.
Switching and Transmission Technologies • 1: Switching Technology • a: Circuit Switching • b: Cell Relay • c: Frame Relay • d: Packet Switching • 2: Transmission Technology: Synchronous Digital Hierarchy ( SDH ) and Synchronous Optical Networks ( SONET ) • 3: ATM: the combination of cell relay and SDH
The History of ATM • 1: the ITU-T and 53 bytes • 2: The perfect mathematical compromise between Europe and American • 3: ATM ( Asynchronous Transfer Mode ) is the first world-wide standard to be embraced by the computer, communications and entertainment industries
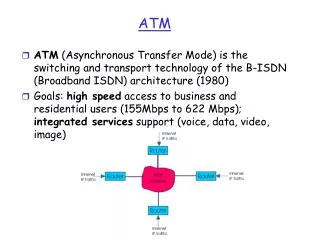
ATM and B-ISDN • 1: Broadband Integrated services Digital Network ( B-ISDN) : the most intelligent of intelligent networks (INs). • 2: ATM is the switching technique at the heart of B-ISDN and makes B-ISDN a reality. • a): ATM can handle any kind of information i.e. Voice, video, image, text, and data in an integrated manner. • b): ATM has high access speeds: 155Mbps,622Mbps and up to 2.4Gbps ( with the backbone carrier networks operating ). • c): ATM provides a flexible use of the bandwidth.
ATM Description(con) • 1: Integrates Voice, Video, Television signals and Data. • 2: Uses short fixed length packets called cells. • 3: Best effort delivery system. • 4: Bandwidth on demand. • 5: Connection Oriented technology -- Every cell with the same source and destination travels over the same route. • 6: Potential to remove performance bottlenecks in today’s LANs and WANs. • 7: Combines local and wide-area networks and services into a seamless whole.
ATM Description(2) • 8: Billing possible on per-cell basis. • 9: Scalable -- Works at different speeds and on different media. • 10: Open-ended growth path -- Not locked to any physical media or speed.
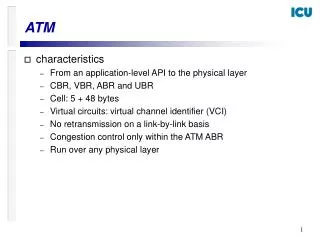
ATM Cell • 1: The basic unit of information transfer in ATM communication. • 2: The cell is comprised of 53 bytes. • 3: Five of the bytes make up the header and the remainder form the user data field.
ATM Cell Header(con) • 1: The main function of the cell header is to carry the VPI and VCI information which allows the active network elements ( ATM multiplexors, switches, crossconnectors ) to switch the cells of active connections through the network. • 2: The cell header comprises 40 bits, of which 24 bits ( in UNI header ) or 28 bits ( in NNI header ) are used for the virtual path and virtual channel identifiers. • 3:The GFC ( Generic Flow Control ) field which is used to control the cell transmission has 4 bits at UNI.
ATM Cell Header(2) • 4: The PT ( payload type ) field which identifies the contents of the cell has 3 bits. • 5: The CLP ( cell loss priority ) bit, when set to 1 means that the cell should be discarded prior to cells where the CLP is set at 0. • 6: The HEC ( header error control ) field comprises 8 bits used for detection of errors in the cell header.
ATM Benefits • 1: One Network • 2: Enables new applications • 3: Compatibility • 4: Incremental Migration • 5: Simplified Network Management • 6: Long Architectural Lifetime
Disadvantage of ATM • 1: Overhead of cell header(5 bytes per cell). • 2:Complex mechanisms for achieving QoS --Quality of Service. • 3:Congestion may cause cell losses.
The Future of ATM(con) • 1: Traditional Local Area Networks ( LANs ) like Ethernet, Token Ring and Token Bus are limited in speed (10mbps) and will not satisfy the need of the future. • 2: For multimedia applications, the bandwidth requirement is high and the information is a combination of Voice, Video and Data and it requires a transfer mode capable of transporting and switching these different types of information. • 3: ATM will play an important role in the broadband communications network of the future
The Future of ATM(2) • 1): FDDI Ring • 2): B-ISDN • 3): Wireless ATM • 4): High Speed Optical Networking(HSON) Using ATM