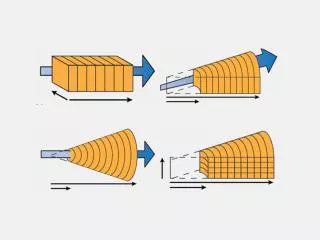
Specify coordinate system on the Domain pane.
70 likes | 192 Vues
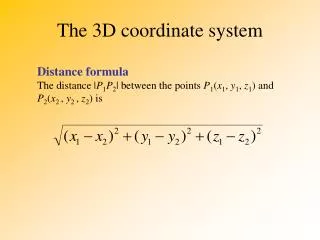
This guide outlines the steps for setting up a coordinate system in fluid flow modeling. You can configure models in linear, radial, or spherical coordinates using X1t, and rectilinear or axisymmetric coordinates using X2t. Key parameters include the number of nodes (Nx, Ny), domain dimensions (length, width), and radius definitions (small-end r1, large-end r2). The coordinate settings will impact the flow field calculations, particularly in axisymmetric domains where fluid velocity is affected by distance from the wellbore.

Specify coordinate system on the Domain pane.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Specify coordinate system on the Domain pane. • Set the number of nodes, Nx. • Set either domain length, x, or grid spacing, ∆x. You can set up a model in linear, radial, or sphericalcoordinates in X1t.
You can set up a model in linear, radial, or sphericalcoordinates in X1t. • Set the number of nodes, Nx. • Set small-end radius, r1 • Set either large-end radius, r2, or grid spacing, ∆r.
You can set up a model in linear, radial, or spherical coordinates in X1t. • Set the number of nodes, Nx. • Set small-end radius, r1 • Set either large-end radius, r2, or grid spacing, ∆r.
Set the number of nodes along y, Ny. • Set either domain width, y, or grid spacing, ∆y. You can set up a model in rectilinear or axisymmetric coordinates in X2t. • Set the number of nodes along x, Nx. • Set either domain length, x, or grid spacing, ∆x.
You can set up a model in rectilinear or axisymmetric coordinates in X2t. • Set the number of nodes along y, Ny. • Set either domain width, y, or grid spacing, ∆y. • Set the number of nodes, Nx. • Set small-end radius, r1 • Set either large-end radius, r2, or grid spacing, ∆r.
X1t and X2t will account for the domain’s coordinate system in calculating the flow field. In an axisymmetric domain, fluid velocity decreases with distance from the wellbore. Large-radius end. Small-radius end.