Color Theory
270 likes | 444 Vues
Color Theory. Ms. Prinkey. What is color?. Color is what the eye sees when light is reflected off an object. The world is full of light. Visible light is made of seven wavelength groups. These are the colors you see in a rainbow: red, orange, yellow, green, blue,

Color Theory
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Color Theory Ms. Prinkey
What is color? • Color is what the eye sees when light is reflected off an object. The world is full of light. Visible light is made of seven wavelength groups. These are the colors you see in a rainbow: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet—the Mr. ROY G. BIV you might have been introduced to in elementary school science. The reddish colors are the long wavelengths. The greenish colors are the mid-size wavelengths. The bluish color are the short wavelengths
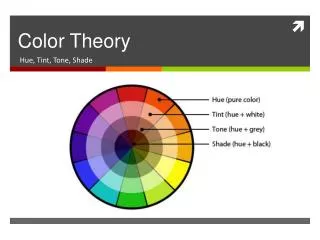
Hue • Hue is a color’s name. • Specifically: Hue is the name of a distinct color of the spectrum—red, green, yellow, orange, blue, and so on. It is the particular wavelength frequency
What is Primary color? • Primary color’s are called “first” colors. • They can be mixed to make all other colors. red yellow blue
What are secondary colors? • They are two primary colors mixed together. + = Red + Blue = Violet + = Red + Yellow = Orange + = Blue + Yellow + Green
What are intermediate or tertiary colors? • Intermediate ( tertiary) colors are the colors in between the primary and secondary colors on a color wheel. • They are a primary color mixed with a secondary color.
Color wheel Yellow + Orange = • A circular arrangement of color which shows the relationship of color. Yellow + Green = Red + Orange = Blue + Green = Red + Violet = Blue + Violet =
Saturation • The "purity" of a color—how much Grey is or isn't in it. • Fully saturated colors are very rich and bright. • 100% blue is a very saturated color (high intensity) • Less saturated colors look muddier, or less pure. • Steel blue has gray undertones (low intensity) Asbjorn Lonvig Danish artist “high intensity” Or very saturated
Low Saturation • Artwork by Daniel Alekow. • Oranges are not pure. • Low saturation or low intensity.
Value • The lightness or darkness of a color. • Tint – when white is added to a color. Makes a light color • Shade – when black is added to a color. Makes a dark color.
“Light in Life, Value Changes” by Tanya Bone. • Show’s changes in the teapot from light to dark. • Where else do you see changes?
Color Schemes • Color schemes are color combinations • Different color schemes have different effects. • Some color schemes may have a loud, disrupting effect, others may be quiet and dull.
Warm color scheme • This scheme can be described as energizing and creating some heat. Warm colors are very active and grab attention. A typical warm color scheme includes red, orange, yellow-orange, yellow and values.
Cool Color Scheme • This scheme can be described as quiet and soothing. A typical cool color scheme would be yellow-green, green, blue-green, blue-purple and values • This one can also be complementary. • Yellow is the complement to purple
Monochromatic Color Scheme • This color scheme consists of one color and black & white. • There are two types of monochromatic color schemes, high contrast values and full range values. • The high contrast value one just uses one color. This color schemes are very good for drawing attention to a particular area of your piece.
The other type is full range values where you select a color and use any additional value of it. This is a monochromatic painting of a cow by Richard E. Adams Monochromatic Color Scheme
Analogous Color Scheme • An analogous color scheme builds from colors that are adjacent colors on the color wheel. • It is one with the most harmony because the colors are right next to each other. • If you use up to four adjacent colors the scheme stays bright.
Complementary • A pair of two opposite colors on the color wheel. • This is a dynamic scheme that offers a nice contrast and tension
Which color scheme are the following pictures? Analogous and Cool
Analogous Warm
Analogous With Complementary Accents