Outline
200 likes | 372 Vues
Security of European Gas Supply What are the important issues for the future? Sylvie Cornot-Gandolphe Principal Gas Expert International Energy Agency GTE 2 nd Annual Conference, 23-24 September 2004. Outline. 1. European Gas Supply/Demand at a Turning Point

Outline
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Security of European Gas Supply What are the important issues for the future?Sylvie Cornot-GandolphePrincipal Gas ExpertInternational Energy AgencyGTE 2nd Annual Conference,23-24 September 2004
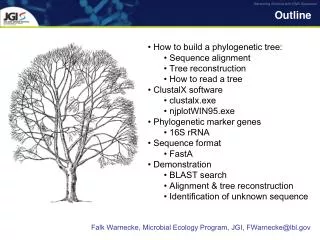
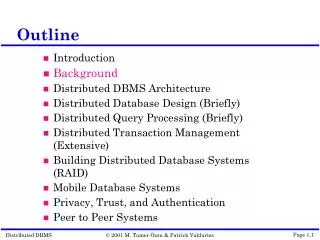
Outline 1. European Gas Supply/Demand at a Turning Point • Growing use of gas in the electricity mix • Growing imports • Imported gas-to-power 2. Major Security of Gas Supply Issues • Growing import dependency/Access to resources • Transit/facility concentration • Substantial gas investment • Investment drivers in open markets • Market fragmentation 3.Conclusion
Gas Demand in OECD Europe Source: World Energy Outlook 2002
OECD European Gas Balance bcm Source: World Energy Outlook 2002
Imported Gas for PowerOECD Europe Source: World Energy Outlook 2002
Drivers/Challenges for gas to power • Drivers for gas to power • Economic growth • Better electric efficiency / environmental performance • Low economies of scale / better fit to open power markets • Uncertainties • Gas/Electricity interface • More market response, but • Risk of domino effect • Volatility of gas prices/high fuel costs • Contractual arrangements • Taxation-CO2 price
Adequacy of Gas SupplyGlobal Gas Reserves by Regions (tcm) Source: Cedigaz
Access to Gas Resources • Revenue sharing:incentives for countries to develop their resources for export • Incentives for investment into export infrastructure • Financing and risk mitigation • Long-term contracts- proven instruments Adaptation to new competitive conditions • JVs/partnerships: integration along the gas chain (physical and financial) • Access to open liquid markets
Transit/Facility concentration • 80% of Russian gas production from three fields (Urengoi, Yamburg and Medvezhye) • The Yamal-Nenets corridor transports 90% of Russian gas • Ukraine transits 80% of Russian gas exports to central and western Europe • Transmed (Algeria/Italy) transports 33% of Italian consumption • GME (Algeria/Spain) transports 30% of Spanish consumption • More than half of Norwegian production and exports from Troll and associated pipelines (Norway). • LNG: 11 regasification terminals in Europe
Substantial investment will be needed Annual gas investment in OECD Europe Source: World Energy Investment Outlook 2003
Price Signals in Open Markets US Spot and Forward Prices – Henry Hub Source: Energy Intelligence
Amber Major pipeline and regas projects
Challenges for Investment in Open Gas Markets • Do not regulate when competition works • US Hackberry decision: LNG terminals not subject to TPA • UK: LNG terminals/BBL exempted from TPA • When regulated, make sure the rate of return is competitive • Do not exclude • long-term contracts • auctions for capacity
Unbundling of Functions/Responsibilities Multiple players, longer chains, more interfaces Unbundling between infrastructure and supply Unbundling of responsibility • Main responsibility vis-à-vis customers AND shareholders • Responsibility for own customers, not the whole market • Coordination of responsibility along the chain Unbundling of investment decisions • Transportation capacity to fit future supplies • Investment incentives for a regulated private business • Investment in insurance assets (for low-probability/high-impact events)
Key messages • The European (and global) supply and demand balance is at a turning point • Markets play their role but cannot play it alone • Governments have an important role: • To define clear security of supply policy objectives (for both supplies and infrastructure) • To define clear responsibility of the various stakeholders • To ensure consistency of the regulatory framework with policy objectives • Leave instruments to the market players • Mix of supply-side instruments, storage, demand-side response, spot and trading instruments