Unraveling the DNA Mystery: From Discovery to Protein Synthesis
570 likes | 594 Vues
Explore the journey of DNA discovery from Fredrick Miescher to Watson and Crick’s double helix structure, including key experiments by Griffith, Avery, Hershey, and Chase. Discover the process of DNA replication, RNA transcription, and protein synthesis essential for life. Dive into the fascinating world of genetics and the human genome.

Unraveling the DNA Mystery: From Discovery to Protein Synthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Discovery of DNA • Fredrick Miescher: (1869) • Discovered a substance that contained phosphorous and speculated that it may contain the hereditary material • Robert Feulgen: (1914) • “feulgen stain” specific to DNA • Nuclei of gametes contain ½ as much • *Fred Griffith: (1928) • Bacterial Transformation • Avery and McCleod: (1944) • Showed that DNA can cause transformation • Hershey and Chase: (1951) • Proved that DNA is the “transforming principle” • Used tagged DNA: p32 and s35
Chromosomes contain Protein DNA ** already known Which one is the “transforming principle” ????? Griffith thought that DNA was the “transforming principle” DNA contains phosphorous Protein contains sulfur *** The debate heated…good science was required! Griffith’s conclusion
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chasewww2.carthage.edu/~pfaffle/hgp/PF.html
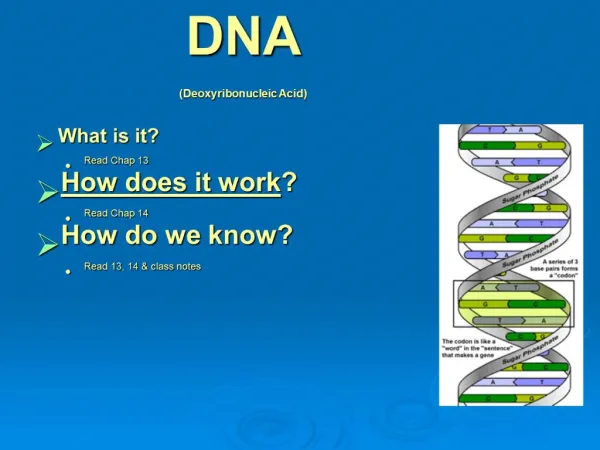
The Structure of DNA“deoxyribonucleic acid” • James Watson and Francis Crick: (1953) • DNA Structure • Deoxyribose sugar: 5-carbon • Phosphate • Nitrogenous base • Purines 1. Adenine 2. Guanine • Pyrimidines 3. Thymine 4. Cytosine
A Nucleotide !! A nucleotide consists of: 1 deoxyribose sugar 1 nitrogenous base 1 phosphate group The percentage of: • Adenine = Thymine • Guanine = Cytosine Genetics is where it’s “AT”
Double Helix 3 5 Mistake with antiparallel!!
Some “DNA Facts” • DNA is double stranded • The two strands run “anti-parallel” • 5’ 3’ ….strand #1 • 3’ 5’ ….strand #2 (complementary strand) • DNA is twisted into a double Helix shape • 46 chromosomes contain approx. 3 billion nucleotides • A series of 3 nucleotides is called a codon or triplet codon • EX: CGA, ATT, CCG, GTA
Try This! What is the complementary base sequence for the following DNA strand? ACT-CGG-GAA-GAT-CTA-TTA-ATT-CGA TGA-GCC-CTT-CTA-GAT-AAT-TAA-GCT
DNA Replication • The DNA double helix unzips • Controlled by enzymes • Each strand serves as a “template” (pattern) • “free nucleotides” fill in and bond to each strand • Replication takes place in the nucleus!!
DNA Replication • Leading Strand: Continuous synthesis • 5’ 3’ direction • DNA Polymerase….proofreads! • Lagging Strand: Discontinuous synthesis • 5’ 3’ ….put together in pieces. DNA Ligase joins fragments
Protein Synthesis DNA controls the production of proteins!!!!!! The “Central Dogma” of genetics – DNA leading to Protein Production DNA makes RNA makes PROTEIN DNA transcription RNA translation PROTEIN DNA RNA PROTEIN • Protein Synthesis occurs in the ribosomes!! • DNA never leaves the nucleus!!
RNA Contains ribose sugar Single stranded Uracil “U” replaces thymine DNA Deoxyribose sugar Double stranded Contains thymine What is RNA?“Ribonucleic Acid”
Try this! What is the complementary strand of RNA for the following strand of DNA? DNA: ATC – GCA – TAT – AAG – GCA – TTC mRNA: UAG – CGU – AUA – UUC – CGU – AAG
Types of RNA • Messenger RNA: (mRNA) Carries a sequence of nucleotides from the nucleus to the ribosomes. • Transfer RNA: (tRNA) Picks up single amino acids in the cytoplasm and “transfers” them to the ribosomes • Ribosomal RNA: (rRNA) Helps bind mRNA and tRNA together….helps make protein!!!
The process where DNA makes RNA 1 strand of DNA serves as a template (pattern) for the production of mRNA. DNA unzips, “free” nucleotides bond to complementary base mRNA will leave the nucleus through a nuclear ______ and carry the “message” to ribosome The process where mRNA gets “translated” into a protein mRNA “codon” is matched with a tRNA “anti-codon” tRNA carries the specific amino acid needed for the polypeptide chain…protein! There are “start’ and “stop” codons!!!! Transcription Translation
“Start and Stop” • Promoter site: sequences in the DNA strand which accept RNA polymerase and initiate transcription • Elongation: mRNA bonds with DNA in small units, transcription bubble, adding bases Adenine to uracil & Guanine to cytosine, etc.. in the 5' to 3' direction (on the new m-RNA). • Termination: stop signal disengages RNA polymerase • RNA polymerase is an enzyme that controls transcription…proofreads.
Try This! Given the DNA code below: 1. List the mRNA made during transcription 2. List the amino acid sequence synthesized during translation/protein synthesis DNA: TTC-ATA-CGG-CGA-ACG-ACT mRNA: AAG-UAU-GCC-GCU-UGC-UGA AA: lysine-tyrosine-alanine-alanine-cysteine-stop
Complete the Table **Use the white board to work with a partner and then transfer your completed answer to paper using a ruler! (QUIZ to FOLLOW)
The Human Genome • Our genome contains approx. 20,000 - 30,000 genes • Craig Venter – 26,000….human genome project • Gene - A discrete section of DNA that codes for a protein…which plays a role in metabolic function • Approx. 2% of our DNA is “functional”….codes for a protein **Comparing DNA Sequences – Bozeman** • Nonfunctional DNA • Pseudogenes or “junk” DNA… today the so-called “junk” DNA is being heavily studied • Remnants of our evolutionary past!
Gene expression & RNA processing • Intron: • Sections of DNA (found on a gene) that do not code for a protein… “intervening” • Exon: • Sections of DNA (found on a gene) that do code for a protein… “expressed” • ****Functional
RNA ProcessingGreat Video on the “Big Picture….gene expression/cell signaling”
Sources of variation • Mutation: A change in a gene or chromosome • Somatic mutation: In the body cells • Affects only the individual possessing it • Germ mutation: In gametes • Occurs during meiosis and can be passed to offspring! • Mutagen: A substance that can cause a mutation ** some mutations are caused by mutagens and others occur spontaneously
Gene/point mutations • Base-deletion: Occurs when a nucleotide is left out • “frame-shift” • Base-insertion: Occurs when an extra nucleotide is added • “frame-shift” • Base-substitution: Occurs when one nucleotide is substituted for another • “missense” Some examples: sickle-cell anemia, albinism
Sickle-Cell Anemia A single base change in the gene for b-globin (hemoglobin) The wrong amino acid is inserted into the polypeptide sequence Results in a protein that becomes distorted under low oxygen conditions 1 allele = malaria resistant 2 alleles = lethal Albinism Individual can’t make enzyme (protein) needed for pigment synthesis No tyrosinase = no melanin production White hair Pink eyes No chlorophyll in plants Gene Mutations
Barbara McClintocktransposons…. “jumping genes” • Jumping genes: • Transposable elements • Transposons • Genes can move around from chromosome to chromosome • They often leave copies before they move • McClintock worked with corn/maize
Chromosomal Mutations • Can occur during mitosis or meiosis • Many are lethal • Many genes are altered • Deletion - removal of a section • Duplication – repeated segment • Inversion – two sections are switched • Translocation – a segment of one chromosome gets attached to a non-homologous chromosome • Non-disjunction
Chromosomal Mutationshttp://staff.jccc.net/PDECELL/evolution/mutations/mutation.html
Non-disjunction • Occurs when homologous chromosomes do not “segregate” or separate properly during anaphase of meiosis • Chromosomal abnormalities can be seen using a karyotype….an illustration of an individuals chromosomes • Trisomy: Having 1 extra chromosome • Monosomy: Having 1 less chromosome
Karyotype Activity http://www.biology.arizona.edu/human_bio/activities/karyotyping/karyotyping.html
Examples of Chromosomal Abnormalities • Down’s syndrome: Trisomy of #21 • Turner’s syndrome: Monosomy of #23 • XO • Female, short in height, sterile • Klinefelter’s syndrome: Trisomy of #23 • XXY • Male, sterile, some mental retardation possible • XYY: “aggressive male syndrome”???
Modern Genetics • Polymerase chain reaction…PCR: • Machine can take a small piece of DNA and replicate multiple copies. • Used in crime labs where small amounts of DNA are found at crime scenes • Electrophoresis/DNA fingerprinting: • Separates DNA by size to identify/create a DNA profile. DNA is run through a gel and is separated by electrical charges • Uses introns…specific to person. Exons are the same!
http://trc.ucdavis.edu/biosci10v/bis10v/week6/6webimages/pcranim.gifhttp://trc.ucdavis.edu/biosci10v/bis10v/week6/6webimages/pcranim.gif • To conduct the PCR reactions researchers mix primers, DNA polymerase, cellular DNA from an organism, and free nucleotides together. • Most DNA polymerase is denatured at high temperature. The polymerase used in PCR (called taq polymerase) is from bacteria that live in hot springs. The bacteria Thermus aquaticus was first isolated from hot springs in Yellowstone National Park.