Joint Net-Centric Operations Strawman
120 likes | 486 Vues
Joint Net-Centric Operations Strawman .

Joint Net-Centric Operations Strawman
E N D
Presentation Transcript
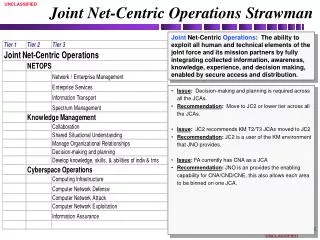
Joint Net-Centric Operations Strawman Joint Net-Centric Operations: The ability to exploit all human and technical elements of the joint force and its mission partners by fully integrating collected information, awareness, knowledge, experience, and decision making, enabled by secure access and distribution. • Issue: Decision-making and planning is required across all the JCAs. • Recommendation: Move to JC2 or lower tier across all the JCAs. • Issue: JC2 recommends KM T2/T3 JCAs moved to JC2 • Recommendation: JC2 is a user of the KM environment that JNO provides. • Issue: FA currently has CNA as a JCA • Recommendation: JNO is an provides the enabling capability for CNA/CND/CNE, this also allows each area to be binned on one JCA.
JNO Seams Seam topic: Potential seam between JNO and CMS “Information Management” Seam with: CMS Recommendation: Coordinate with CMS to clarify the definition and intent of “Information Management” Rationale: The CMS “Information Management” definition as written, encompasses many of the capabilities currently within NC Recommended business rule: None at this time Seam topic: Potential seam between NC “Information Transport” and BA “Dissemination and Integration” Seam with: BA Recommendation: Drop “Dissemination” from BA definition. Rationale: “Dissemination” is a capability in NC Recommended business rule: None at this time
JNO Seams - concluded Seam topic: Duplication/overlap between JNO “Develop knowledge, skills, and capabilities of individuals and teams” and FS “Training” and “Education” Seam with: FS Recommendation: Drop “Develop knowledge, skills, and capabilities of individuals and teams” from NC. Rationale: “Develop knowledge, skills, and capabilities of individuals and teams” appropriately addressed in FS “Training” and “Education”, consistent with the JCABR guiding principles, need not be duplicated in JNO Recommended business rule: None
JNO Tier 2 & 3 Definitions • NETOPS: The ability to provide assured net-centric services across the full spectrum of operations throughout the Global Information Grid (GIG) enterprise, seamlessly, securely and end to end. • Network/Enterprise Management: The ability to provide the network with the desired level of quality, agility, and trustworthiness; including the planning coordinating and managing DOD use of the electromagnetic spectrum (EMS) through operational, engineering and administrative procedures. NM focuses on the configuration, availability, performance and manageability of network services and the underlying physical assets that provide end-user services, as well as connectivity to enterprise application services. (Modified Joint Concept of Ops for GIG NETOPS/JP 6-0) • Enterprise Services (ES): The ability to provide well-defined enterprise network functionality that accepts a request and return a response through an interface with a user or another service, such as collaboration, messaging, or information discovery. (NCE JFC/NCOE JIC) • Information Transport (IT): The ability to provide end-to-end communications media over which assured connectivity takes place, supported by switching and routing systems. (NCE JFC/NCOE JIC) • Electromagnetic Spectrum Management (EMS): Planning, coordinating and managing joint use of the EMS though operational, engineering and administrative procedures. The objective of SM is to enable electronic systems to perform their functions in the intended environment without causing or suffering unacceptable interference. (JP 6-0)
JNO Tier 2 & 3 Definitions • Knowledge Management (KM): The ability to create an environment to systematically discover, select, organize, distill, share, develop, and use information in a social domain context to improve warfighter and business effectiveness. (Modified NCE JFC/NCOE JIC) • Collaboration: The ability to continuously include geographically separated participants, involving all relevant parties in a virtual space that utilizes collaboration tools and visualization techniques to share knowledge and support decision-making. • Organizational relationships: The ability to set-up and change formal organizational and command relationships according to mission and task needs. The NCOE supports existing frameworks and provides a new COI framework for formal and informal organizational needs. • Share situational understanding: The ability to share understanding with an array of participants, will lead to better collective understanding and contribute to higher quality decision-making. Through the use of KM tools, sharing situational understanding will be enhanced. • Decision-Making and Planning: The ability to provide adaptive, distributed, cooperative, and collaborative decision-making and planning. Many elements will be involved in decision-making. Decision-makers require collaboration tools and sophisticated decision-support tools that recognizes that a variety of different methods could be needed, especially for a variety of environments, circumstances, and missions.(Possible move to C2). • Develop knowledge, skills, and abilities of individuals and teams: The ability to develop knowledge, skills, and abilities through effective collaborative training methods. The dynamic nature of the future environment will require that teams be established with little or no previous working relationships. As a result, training will need to be conducted en route to the operating area. The use of collaborative and interactive training will enable effective training to be accomplished in minimal time.
Cyberspace Operations: A domain characterized by the use of electronics and electromagnetic spectrum to store, modify, and exchange data via network systems and associated physical infrastructure. Computing Infrastructure (CI): The ability to provide dynamic and scalable automated IT resources; i.e., hardware, software operating systems, and hardware/software operating systems support; which are used in the secure acquisition, storage, processing, manipulation, management, control, and display of data / information, have NetOps situational awareness, and enable visibility, accessibility, understandable, trusted access to data / information and shared IT resources. Computer Network Defense (CND): The ability to protect, monitor, analyze, detect and respond to unauthorized activity within Department of Defense information systems and computer networks through the use of computer networks. (JP 3-13) Computer Network Attack (CNA): The ability to disrupt, deny, degrade, or destroy information resident in computers and computer networks, or the computers and networks themselves through the use of computer networks. (JP 3-13) Computer Network Exploitation (CNE): The ability to enable operations and intelligence collection capabilities conducted through the use of computer networks to gather data from target or adversary automated information systems or networks. (JP 3-13) Information Assurance (IA): The ability to provide the measures that protect and defend information and information systems by ensuring their availability, integrity, authentication, confidentiality, and non-repudiation. This includes providing for the restoration of information systems by incorporating protection, detection, and reaction capabilities. (DOD Directive 8500.1 “Information Assurance”) JNO Tier 2 & 3 Definitions 7
JNO Tier 4 • Network/Enterprise Management (T3): • Optimized network functions and resources: The ability to dynamically control and manage assigned network resources such that their availability and functionality, including degraded modes, are continuously optimized to mission needs and to dynamically acquire and incorporate additional network resources when required. • Enterprise Services (T3): • Accessible and useful data and information: The ability to filter, fuse, and correlate data and information into useful forms. Users must be able to locate the required data and information and to extract it. • Identify, store, share, and exchange data and information: The ability to perform all actions necessary to store, publish, and exchange information and data. Data must be appropriately identified and labeled (tagged), placed in a database or other data/information repository, and its presence announced to those who need it (post/publish/advertise). • Information Transport (T3): • Deploy scalable and modular networks: The ability to design, assemble, transport, deploy and establish mission-scaled networks from adaptable component network modules, composed of physical media, configurable module equipment, software, and associated operational resources for required fixed or mobile network nodes or network links. • Information End to End transport:The ability to accurately transmit and receive information over networks in time to meet mission requirements, with minimum location, spectrum, or bandwidth constraints on the user.
JNO Tier 4 • Computing Infrastructure(T3): • Distributed CI functionality for data and information sharing: The ability to provide modular, deployable computing infrastructure that enables trusted users to access and share data and information efficiently and effectively anywhere they are located, across functional, security, national, and interagency domains. • Dynamic CI processing and data storage: The ability to provide secure, dynamic, and transparent provisioning and allocation of storage and processing resources, from pooled infrastructure, resources to any user, based on usage patterns and real-time capacity requests, regardless of location, connectivity, or user network access device. • Adaptive hosting environments for applications and COI services: The ability to provide to users, dynamically and transparently, hosting environments that are adaptive to location, bandwidth limitations, demand, hardware, software operating systems, various types of applications (software, mission-specific), various types of community of interest (COI) services (legacy, service-oriented architecture), and other applications and services characteristics.
JNO Tier 4 • Information Assurance (T3): • Secure Information Exchange: The ability to securely and dynamically share information between communities of interest, protected from modification, ensure only authorized user access, share user access rights across the enterprise, and provide assured information discovery and retrieval for sharing information across domains. • Protected Data and Networks: The ability to prevent successful data attacks by monitoring the IA status of the GIG; tracking identities, privileges, and actions of users; ensuring information integrity; and, by using encryption to provide confidentiality that assures information is only disclosed to authorized users. Prevents successful network attacks by employing information control zones, network access controls, and host based data encryption security. Provides for flexible allocation of resources for mission needs. • Attack / Event Response: The ability to provide intrusion prevention and situational awareness systems that detect and respond to attacks, defend the GIG, maintain services while under cyber-attack, recover from cyber-attack, and ensure availability of information and systems.