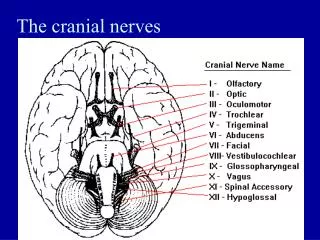
The cranial nerves
240 likes | 813 Vues
The cranial nerves. Central Nervous System - Brain. Identify the anatomical location of each major brain area. Describe the functions of the major brain areas including specialized subregions. Major brain areas. Cerebrum * cortex * basal ganglia * limbic system. Thalamus:

The cranial nerves
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Central Nervous System - Brain • Identify the anatomical location of each major brain area. • Describe the functions of the major brain areas including specialized subregions.
Major brain areas Cerebrum * cortex * basal ganglia * limbic system Thalamus: sensory relay station Cerebellum:* motor coordination* balance Hypothalamus autonomic NS Brain stem:* midbrain * pons * medulla Reticular formation arousal/sleep/wake
Cerebral Cortex: Perception of senses, association, reasoning, information integration, planning, directing voluntary behavior
Figure 48.25 Primary motor and somatosensory areas of the human cerebral cortex
Map this pathway as a simple afferent to CNS to efferent path, naming the neural structures involved:“You feel the desk and move your hand away as soon as you feel the desk.”
somatosensory cortex to primary motor cortex Touch receptors thalamus spinal cord sensory neuron Somatic motor nerve to muscle
Spinal Cord Dorsal root - sensory Ventral root - motor The white matter consists of ascending (green) and descending (red) axons while the gray matter contains primarily dendrites and cell soma. Each segment has paired spinal nerves. 31 total
Cerebrum - basal nuclei and limbic system • Basal nuclei –control of movement • Limbic System • Cingulate gyrus –role in emotion • Hippocampus –learning & memory • Amygdala –emotion & memory Figure 9-13: The limbic system
Diencephalon -thalamus & hypothalamus • Thalamus – relay & sensory integration • Hypothalamus • Homeostatic control centers • Motivated behavior control • Hunger, stress • Thirst: body osmolarity • Autonomic NS control • Emotional input • Circadian rhythms • Tropic for endocrine
Complex function: Language Figure 9-23: Cerebral processing of spoken and visual language
Damage to Broca's Area (Broca's aphasia) - prevents a person from producing speech - person can understand language - words are not properly formed - speech is slow and slurred. Damage to Wernicke's Area (Wernicke's aphasia) loss of word understanding person can speak clearly, but the words make no sense.
Cerebrum Figure 9-11: The basal nuclei Figure 9-16: Cerebral lateralization