Complex patterns of inheritance
180 likes | 345 Vues
Complex patterns of inheritance. Section 12.2. Incomplete dominance. Phenotype of heterozygous individuals is intermediate between those of the 2 homozygotes. Incomplete Dominance example. Codominance.

Complex patterns of inheritance
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Complex patterns of inheritance Section 12.2
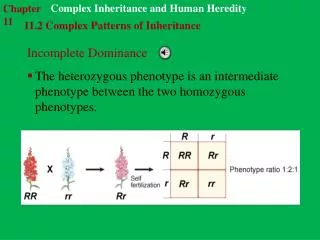
Incomplete dominance • Phenotype of heterozygous individuals is intermediate between those of the 2 homozygotes.
Codominance • Phenotypes of both homozygotes produced in heterozygous individuals. (both alleles expressed equally).
Multiple Alleles • An inheritance pattern in which traits are controlled by more than 2 alleles
Multiple Alleles example IA IA IA Ii
Sex Determination • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes
Sex Determination • Of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, 22 are autosomes (pairs that look alike) and 1 are sex chromosomes.
Sex Determination • A karyotype is a diagram of the chromosomes (arranged in order for study)
Sex Determination • Sex chromosomes are indicated by the letters X and Y • Females sex chromosomes are XX • Male sex chromosomes are XY • Who controls the sex of offspring? • Males (Sperm) • Why? • All female eggs carry X chromosome. Sperm carry X or Y
Sex-linked inheritance • Sex-linked traits: characteristics determined by genes on sex chromosomes • Can sex-linked traits be on the X or Y chromosome? • Yes • Which is more common? • X chromosome
Sex-linked inheritance • Alleles are written as superscripts for X and Y for sex linked traits • What does it look like? • XRXr or XrY
Color Blindness • C = normal • c = color blind • Male with color blindness = XcY • Female with color blindness = XcXc
Color Blindness • Female carrier of color blindness = XCXc • Normal (non-carrier) = XCXC • Why can only females be carriers of X-linked traits? • Males only have one X-chromosome. If the trait is on the X chromosome they will be colorblind. • Can males or females pass on y-linked traits? • Only males
Practice Hemophilia is a lethal recessive sex linked trait. It causes your blood to be unable to clot. So, if you fall and cut your chin open, the blood will keep spurting out of your chin! If Queen Victoria carries a recessive trait for hemophilia XHXh and marries Albert who has hemophilia XhY. How many of their children will die from hemophilia?
Polygenic traits • Traits caused by more than one gene