Vector data model
170 likes | 189 Vues
Explore the differences between hybrid and integrated systems for vector data models, which store spatial and attribute data in separate or integrated ways. Learn about address matching, the process of correlating street addresses with geographic coordinates, and the challenges that arise from inconsistencies between the geodatabase and address lists.

Vector data model
E N D
Presentation Transcript
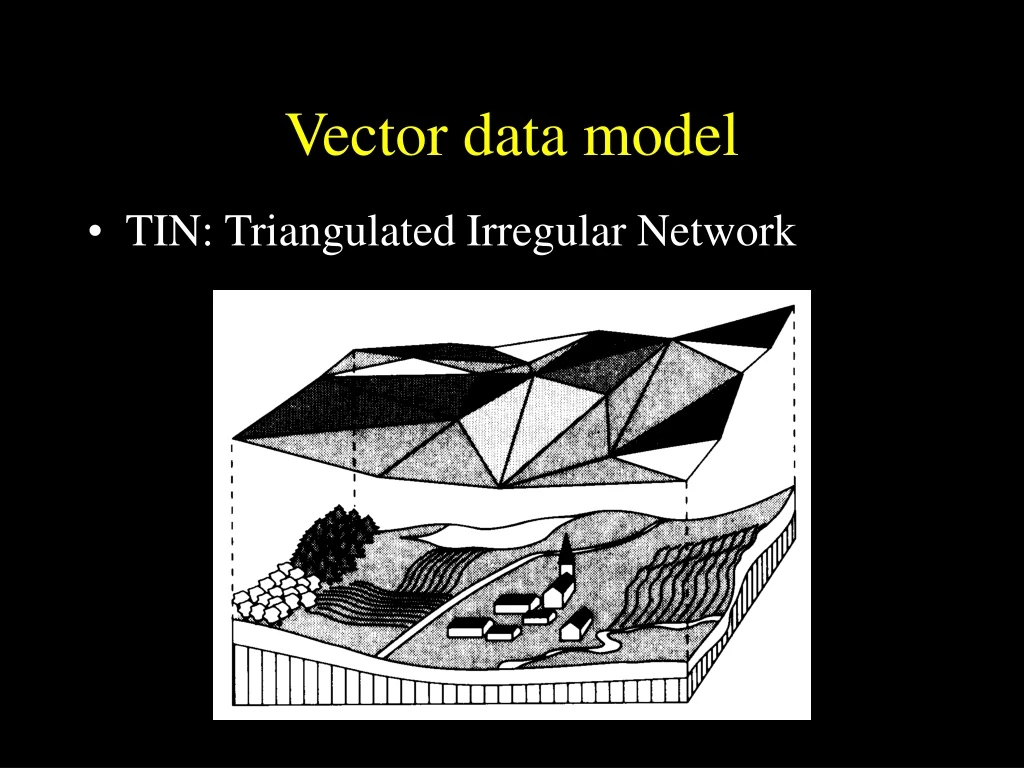
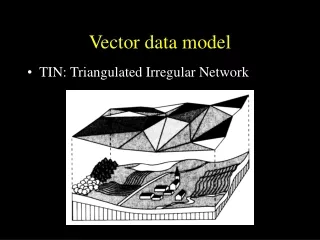
Vector data model • TIN: Triangulated Irregular Network
Vector data model TIN: Triangulated Irregular Network
Vector data model • TIN: Triangulated Irregular Network
Vector data model • Hybrid vs. integrated systems for vector data models • A hybrid system stores spatial data in one type of data model and the attribute data in another data model that is often an existing commercial non-spatial database • An integrated system manages both spatial and attribute data using the same data model
E B A D C F ID Length Key A 5 1 B 6 2 C 6 2 D 7 1 E 9 1 F 9 3 Key Name Length 1 Main St. 21 2 Elm St. 12 3 Spruce St. 9
Address Matching • Address matching is the process of correlating an input street address with a street segment in an underlying geographic database. Once found, geographic coordinates are interpolated within the matching segment and census codes are copied from the matching segment to the input street address.
Address Matching • Why address match? • find the location of an event which has been recorded at a street address • identify the political and administrative areas to which it belongs.
What is an address matched record? • Address-matched locations are usually recorded (after the address is located) as unique latitude and longitude coordinates.
How is address matching done? • One file is a digital street map which describes the locational coordinates of the centerline of all streets, the range of street addresses that are found on each street segment. (Geometry) • The second file contains the street descriptions of the events which are to be address-matched. (Attributes)
Road Network to a Centerline • After a road network has been abstracted it is now represented by cells. • These cells can be catagorized as either 0 cells or 1 cells. • Where a 0 cell is a node and is an intersection of 1 cells. • The line that connects two nodes is a 1 cell.
Locating Addresses General Process 1. Match street.2. Find street segment that contains address within its range name.3. Interpolate location between bounding 0-cells.
What are the problems? • Address-matching is rarely a fully automated, computerized process. • An address may not address-match because of inaccuracies or inconsistencies in the digital street map or because of inaccuracies or inconsistencies in the file of addresses to be matched. • Address-matching rates (the proportion of addresses that are correctly matched) will increase if efforts are made to increase the quality of the digital street map, the address file, or both.