Retinal Scan
240 likes | 494 Vues
Sami Lyden. Retinal Scan. Presentation. Biometrics Method Advantages Disadvantages Retinal recognition Scanners Methods Comparison Developement?. Biometrics: Eye. Eye is fully developed at birth Doesn't significally chage during life Individually unique pattern of veins at retina

Retinal Scan
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sami Lyden Retinal Scan
Presentation • Biometrics • Method • Advantages • Disadvantages • Retinal recognition • Scanners • Methods • Comparison • Developement?
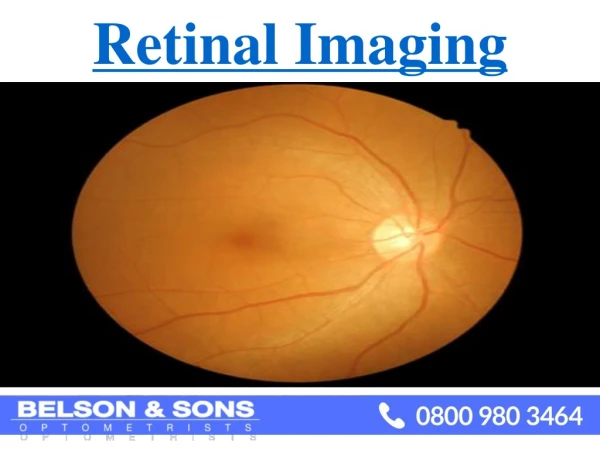
Biometrics: Eye • Eye is fully developed at birth • Doesn't significally chage during life • Individually unique pattern of veins at retina • Vein patterns and intersections are fixed • Veins emanate from the optic nerve • Method dates to 1930's
Biometrics: Advantages • Isolated biometrics • Difficult to reach • Easy to read • Insignificant interference • Stable • Unique • Protected • Insensitive to environmental conditions • Extremely accurate verificator Twin A Twin B
Biometrics: Disadvantages • Difficult to reach • There are no completely non-intrusive scanning methods • Very little development in the area • Medical scanners are made for accurasy • There is huge amount of usable identification data but current methods only use very small portion of it • Resources are directed to other methods • Eye is vulnerable to disease and trauma • Most(?) scanners now require interaction (eye focus and direction)
Recognition: History • First automated retinal scanner and indentifier was patented 1977 by Robert B. Hill • Used green diodes to reflect light from the fundus • The light reflected from blood vessels was identified and mapped for recognition Eye Dentify's Retinal scanner, 1989.
Recognition: History (cont.) • System first detected the optic nerve • Then scanned the region using 360 diodes • Veins are then mapped as features • Acuired data is very simple. The verification process is very fast
Recognition: History (cont.) • The scanner is replaced by infrared Laser scanners during 80's • Scanners still require the target to remain very close to scanners • The scanners are large complicated and expensive. Koji Kobayashi's scanner Robert H. Webb's scanner
Recognition: History (cont.) • First scanners also used lasers with so high energy that some left the target dazed after the scan • Other more lucrative methods replace the retinal scanning as more user friendly • Almost all resources are diverted to other biometrics study • Only research is done in private high security installations. (If any) • Scanners are still developed for medical purposes
Retinal Recognition: New Beginning? • Retinal Technologies, is a company that has developed medical scanners has come up with new method derived from those medical scanners. • Entire retina is illuminated at once using infrared laser.
Comparison • The data is very simple. Allows quick 1:N searches • Data is also very accurate which allows effective 1:1 comparison • Almost no unwanted interfering data • Very few comparison tests are available • No exact up to date FAR's or FRR's available • Still the method is considered the most accurate method of all Biometrics
Comparison (cont.) Crossover error Fingerprint 1 in 500 Hand Geometry 1 in 500 Speaker Recog. 1 in 50 Iris Scan 1 in 131,000 Retinal Scan 1 in 10,000,000 Signature Recog 1 in 50 ---------------------------------------- Statistics are from National Center for State Courts(US) and Biometric Technology, Inc Web pages (rev 2002) • Biometric data allows very accurate verification • Problem is the scanner. • They currently operate at 1m distance • Retinal scanners are used at High-End security installations
Comparison (cont.) • Forging fake retina is virtually impossible • Bloodvessels quickly deteriorate after death • 1:1 verification is still possible after death • Infrared scanner could be used to detect blood flow at the vessels • Other methods could be used to verify the eye is living • Scanning operation also requires for the eye to focus at the reader
Comparison (cont.) • Retinal scanning is not influensed by out side interference • lighting, aging, injury, air conditions, temperature... • People naturally protect their eyes • Smaller chance for injury • People wont be able to accept the idea of laser beam being fired into the eye. (never)
Retinal Scanners • There are 2 players at the market currently • Eye Dentify is the main suplier of retinal scanners • They don't produce final security products but use re-sellers • Retinal Technology has produced a new method
Retinal Scanners • Both scanners are fast • Eye Dentify's take less than 2sec for scan • They are insensitive to environmental conditions • (claim to be. Wonder if they workoutside when its raining) • Both work up to 3' (1m) • Cost effective • According to the manufacturers. I coudn't find any actual prices..
Retinal Technologies • On April 1st, 2002, Retinal Technologies received a notice of allowance from the US patent office. • Method for generating a unique and consistent signal pattern for identification of an individual • Exact data of the above method is not currently available • Also owns other patents for medical retinal scanners
Retinal Technologies • The scanning method for Retinal technologies is similar to that of the Eye Dentify • Scanning works in 4 steps • First the intensity profile is extracted • Step two: A scan
Retinal Technologies • Step Three: The blood Veins are located • Step Four: A Circular Bar Code is generated from the veins • This produces a relatively short data template
Future? • One of the problems for Retinal Scanning is that the method for identifying has been extremely efficient but the scanner have been expensive and intrusive so this has not been a very lucrative method and recourses have been placed elsewhere • The scanners have been developed for medical purposes -> they have become faster and smaller • But the problem of intrusiveness remains. • Still as a highly accurate method that cannot be fooled the high security installations will continue to use and possibly develope the scanners
US Patent and Trademark Office. Patent Database: http://www.uspto.gov/patft/index.html (patents:) Biometric Technology, Inc http://www.bio-tech-inc.com/ Eye Dentify, Inc (Currently no Web-pages) Retinal Technologies, LLC http://www.retinaltech.com/ Key References