Dynamic Networks, Influence Systems, and Renormalization
600 likes | 724 Vues
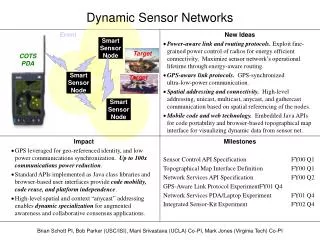
This work by Bernard Chazelle delves into the interplay between dynamic networks and influence systems, highlighting models where interacting agents operate under distinct physical laws and communication rules. It explores Hegselmann-Krause systems, authoritarian and libertarian roles, and their implications in a dynamic network. With 20,000 agents adapting weights to converge towards the weighted mass center of neighbors, the study examines chaotic behaviors, phase transitions, and the challenging predictability of long-range dynamics within these complex systems.

Dynamic Networks, Influence Systems, and Renormalization
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Dynamic Networks, Influence Systems, and Renormalization Bernard Chazelle Princeton University
Interacting particles, each one with its own physical laws !
authoritarian left right libertarian
authoritarian left right libertarian
authoritarian left right libertarian
authoritarian left right libertarian
Each agent chooses weights and moves to weighted mass center of neighbors
Communication rules network Dynamical rules here, averaging
Communication rules network Eliminate quantifiers (Tarski-Collins)
Interacting particles, each with its own communication laws!
Dynamical rules ( must respect network) eg, Ising model, swarm systems, voter model
Influence systems Very general !
Diffusive Influence systems deterministic convexity
Dynamical system in high dimension stochastic matrix Dynamic network associated with P (x)
What if all the matrices are the same? fixed-point attractors or limit cycles
Theory of diffusive influence systems Theory of Markov chains
Results Diffusive influence systems can be chaotic All Lyapunov exponents are
Results Diffusive influence systems can be chaotic Random perturbation leads to a limit cycle almost surely Phase transitions form a Cantor set Predicting long-range behavior is undecidable
Bounding the topological entropy via algorithmicrenormalization
Grammar Language