Color Theory and Space
200 likes | 430 Vues
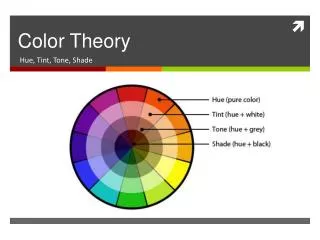
Color Theory and Space. Carty 2013. Color. An element of design with three properties: hue, value, and intensity. Also the character of surfaces created by the response of vision to wavelengths of reflected light. Hue.

Color Theory and Space
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Color Theory and Space Carty 2013
Color • An element of design with three properties: hue, value, and intensity. Also the character of surfaces created by the response of vision to wavelengths of reflected light.
Hue • The property of a color that distinguishes one gradation from another and gives it its name. • For example: Hue would identify colors on the color wheel of spectrum as blue, green, yellow, or red as they are seen.
Primary Colors • The three basic colors, red, yellow, and blue, from which it is possible to mix all other colors. The primaries cannot be produced by mixing pigments.
Secondary Colors • Colors that result from the mixture of two primary colors. On the twelve color-wheel: orange, green and violet.
Intermediate Colors • Colors produced by mixing a primary colors and the adjacent secondary colors on the color wheel. (For example: yellow-green, or red-orange) They are also made by mixing unequal amounts of two primaries. (For example: by mixing yellow and blue, with a majority of yellow, one would yield yellow-green)
Complementary Colors • Two colors which are directly opposite to each other on the color wheel, meaning they are in extreme contrast with each other.
Monochromatic • One color which is modified by changing the values and saturation of the hue by additions of black and white.
Intensity • The degree or purity, saturation or strength of a color. High intensity colors are bright; low intensity colors are dull.
Triadic Color Scheme • Any three colors equidistant on the color wheel.
Split Complementary • On the color wheel, a hue which is combined with hues on either side of its complement.
Analogous Colors • Colors that are next to each other on the color wheel and are closely related, such as yellow, yellow-orange, and orange.
Space • An element of art that indicates areas between, around, above, below, or within something. • The element of space that is defined by the interior space of an object or room is called volume.
Da Vinci and Space • Leonardo DaVinci used several types of perspective to give his paintings a sense of space: atmospheric perspective, which shows objects and the air appearing bluer and hazier as they get farther away; diminishing perspective, which shows objects decreasing in size the farther away they are from the viewer; and one-point perspective, which uses mathematical principles to show lines that recede from the viewer getting closer together as they converge towards a vanishing point on the horizon.
Linear Persepctive • A technique of creating the illusion of depth on a flat surface. All parallel lines receding into the distance are drawn to converge with one or more vanishing points on the horizon line.
Vanishing Point • The vanishing point in a work of art which displays liner perspective is the point on the horizon line at which receding lines converge to create the illusion of depth
Horizon Line • The horizon line in a work of art which displays linear perspective is the horizontal line on which vanishing points are located and to which receding lines converge.
Aerial Perspective • The diminishing of color intensity to lighter and duller hues to give the illusion of distance.